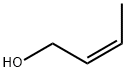
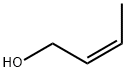
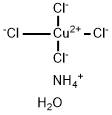
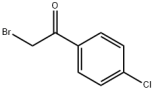
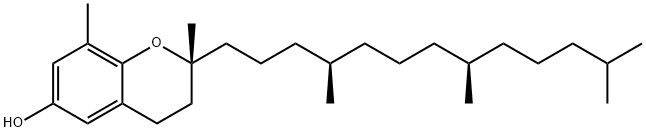
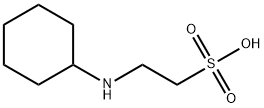
CIS-2-BUTEN-1-OL literature
Reductive Cleavage of 5,6-Dihydro-2H-pyran Derivatives; Facile Synthesis of cis-3-Hexenol
Kobayashi, Toyohiko,Tsuruta, Haruki
, p. 492 - 493 (1980)
-
A comparison between conventional and ultrasound-mediated heterogeneous catalysis: Hydrogenation of 3-buten-1-ol aqueous solutions
Disselkamp,Judd,Hart,Peden,Posakony,Bond
, p. 347 - 353 (2004)
A power flow scheme applicable to probe-type ultrasound reactors is presented, that has been deduced from both theoretical estimates and experimental measurements employing a thermal insulated vessel. Under typical conditions for water at 1 atm pressure, 77% of the electrical power is converted into mechanical motion of the probe, that in turn is dissipated to both acoustic power (~12%) and cavitational heating (~88%). Approximately 92% of the mechanical power of the probe was converted into heat, with the remaining power presumably converted into audible acoustic and/or mechanical motion. In a second type of experiment performed here, heterogeneous catalysis experiments have been performed at 298 K in an isothermal (i.e., jacketed) reaction vessel comparing chemistry in conventional (e.g., thermal) versus ultrasound-assisted systems. Both product state distribution and reaction rate measurements have been performed for the hydrogenation (using hydrogen gas) of aqueous 3-buten-1-ol solutions employing Pd-black powder. Products from the heterogeneous catalysis include isomerization to cis- and trans-2-buten-1-ol, as well as hydrogenation to 1-butanol. A reaction scheme involving surface-bound alkyl-radical species, consistent with previous published work, is proposed to explain product formation. Based on the observed differences in cis- to trans-2-buten-1-ol ratios in conventional versus ultrasound experiments, employing untreated and prereduced catalysts, it has been determined that ultrasound creates catalyst site(s) enhancing the cis-to-trans 2-buten-1-ol ratio from 0.25 to 0.55. In addition, comparing the total isomerization to hydrogenation ratio (cis- plus trans-2-buten-1-ol to 1-butanol ratio), for ultrasound-assisted and conventional catalysis, reveal a ~5-fold enhancement in isomerization relative to the more energetically favored hydrogenation due to the application of ultrasound. Finally, the product formation rates for 1-butanol, as well as isomerization plus hydrogenation, revealed that conventional and ultrasound experiments showed both a nonlinear dependence with applied ultrasound power and no differences between untreated and prereduced catalysts. The observed reaction rate enhancements were 1:36:183 for the conventional, 90 W ultrasound, and 190 W ultrasound experiments, respectively.
Deconvoluting the memory effect in Pd-catalyzed allylic alkylation: Effect of leaving group and added chloride
Fristrup, Peter,Jensen, Thomas,Hoppe, Jakob,Norrby, Per-Ola
, p. 5352 - 5360 (2006)
An analysis of product distributions in the Tsuji-Trost reaction indicates that several instances of reported "memory effects" can be attributed to slow interconversion of the initially formed syn- and anti- [Pd(η3-allyl)] complexes. Addition of chloride triggers a true memory effect, in which the allylic terminus originally bearing the leaving group has a higher reactivity. The latter effect, termed regioretention, can be rationalized by ionization from a palladium complex bearing a chloride ion, forming an unsymmetrically substituted [Pd(η3-allyl)] complex. DFT calculations verify that the position trans to the phosphine ligand is more reactive both in the initial ionization and in the subsequent nucleophilic attack.
Non-Cryogenic, Ammonia-Free Reduction of Aryl Compounds
-
, (2022/03/31)
A method of reducing an aromatic ring or a cyclic, allylic ether in a compound includes preparing a reaction mixture including a compound including an aromatic moiety or a cyclic, allylic ether moiety, an alkali metal, and either ethylenediamine, diethylenetriamine, triethylenetetramine, or a combination thereof, in an ether solvent; and reacting the reaction mixture at from ?20° C. to 30° C. for a time sufficient to reduce a double bond in the aromatic moiety to a single bond or to reduce the cyclic, allylic ether moiety.
Total Synthesis of Mycinolide IV and Path-Scouting for Aldgamycin N
Herlé, Bart,Sp?th, Georg,Schreyer, Lucas,Fürstner, Alois
supporting information, p. 7893 - 7899 (2021/03/03)
Proof-of-concept is provided that a large estate of 16-membered macrolide antibiotics can be reached by a “unified” approach. The key building block was formed on scale by an asymmetric vinylogous Mukaiyama aldol reaction; its alkene terminus was then converted either into the corresponding methyl ketone by Wacker oxidation or into a chain-extended aldehyde by catalyst-controlled branch-selective asymmetric hydroformylation. These transformations ultimately opened access to two structurally distinct series of macrolide targets. Notable late-stage maneuvers comprise a rare example of a ruthenium-catalyzed redox isomerization of an 1,3-enyne-5-ol into a 1,3-diene-5-one derivative, as well as the elaboration of a tertiary propargylic alcohol into an acyloin by trans-hydrostannation/Chan-Lam-type coupling. Moreover, this case study illustrates the underutilized possibility of forging complex macrolactone rings by transesterification under essentially neutral conditions.
Molecular Recognition and Cocrystallization of Methylated and Halogenated Fragments of Danicalipin A by Enantiopure Alleno-Acetylenic Cage Receptors
Carreira, Erick M.,Diederich, Fran?ois,Fischer, Stefan,Gropp, Cornelius,Husch, Tamara,Trapp, Nils
supporting information, (2020/03/13)
Enantiopure (P)4- and (M)4-configured alleno-acetylenic cage (AAC) receptors offer a highly defined interior for the complexation and structure elucidation of small molecule fragments of the stereochemically complex chlorosulfolipid danicalipin A. Solution (NMR), solid state (X-ray), and theoretical investigations of the formed host-guest complexes provide insight into the conformational preferences of 14 achiral and chiral derivatives of the danicalipin A chlorohydrin core in a confined, mostly hydrophobic environment, extending previously reported studies in polar solvents. The conserved binding mode of the guests permits deciphering the effect of functional group replacements on Gibbs binding energies ΔG. A strong contribution of conformational energies toward the binding affinities is revealed, which explains why the denser packing of larger apolar domains of the guests does not necessarily lead to higher association. Enantioselective binding of chiral guests, with energetic differences ΔΔG293 K up to 0.7 kcal mol-1 between diastereoisomeric complexes, is explained by hydrogen- and halogen-bonding, as well as dispersion interactions. Calorimetric studies (ITC) show that the stronger binding of one enantiomer is accompanied by an increased gain in enthalpy ΔH but at the cost of a larger entropic penalty TΔS stemming from tighter binding.
SYNTHESIS OF (2S,3R,4R)-4,5-DIHYDROXYISOLEUCINE AND DERIVATIVES
-
Page/Page column 23, (2019/10/19)
The invention relates to a method for the preparation of a 4,5-dihydroxyisoleucine derivative comprising the steps of asymmetric Claisen rearrangement of a Z-aminocrotyl-glycin ester and subsequent kinetic resolution of the product diastereomer mix by acylase, and subsequent Sharpless dihydroxylation of the resulting 2-amino-3-methylpent-4-enoicacid derivative.