D-Tartaric acid literature
Preparation method of 2-amino-5-bromopyridine
-
Paragraph 0016; 0038-0046, (2020/05/05)
The invention belongs to the technical field of organic synthesis, and specifically relates to a preparation method of 2-amino-5-bromopyridine. The method comprises the following steps: 2-aminopyridine serves as a raw material, dichloromethane or trichloromethane serves as a solvent, 2-aminopyridine and phenyl trimethyl ammonium tribromide carry out reactions for 1-3 hours at the temperature of 20-50 DEG C, and the molar ratio of 2-aminopyridine to phenyl trimethyl ammonium tribromide is 0.7-1.4. The preparation method provided by the invention has the beneficial effects that (1) the generation of a large number of 3-position byproducts in a traditional preparation method is avoided, and the waste of raw materials and the load of subsequent separation are reduced; and (2) the raw materialnamely 2-aminopyridine is easy to obtain and low in cost, the synthesis route has the advantages of high yield and mild conditions, no 3-position byproduct is generated in the whole process, and the preparation method has an industrialization prospect.
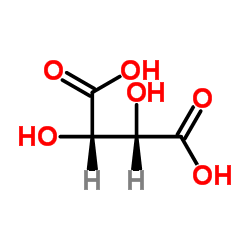
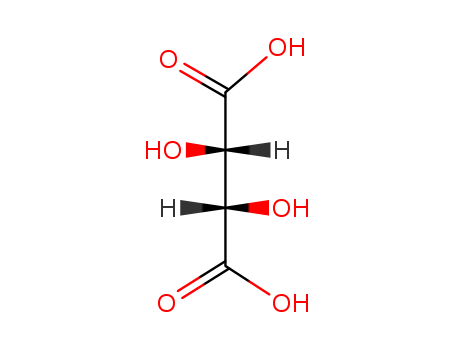
Novel preparation method D-(-)- tartaric acid
-
Paragraph 0016; 0038-0046, (2020/05/05)
The invention discloses a new preparation method for D-(-)-tartaric acid, and relates to the preparation method of the resolving agent D-(-)-tartaric acid widely applied in the field of pharmaceuticalsynthesis. The method includes the following steps successively: taking (2R,3R)-2,3-diethyl dihydroxy succinate as a raw material, after hydroxyl protection, substituting with an acetoxyl group, andfinally, carrying out hydrolysis reaction to obtain D-(-)-tartaric acid. The invention provides a new route comprising the steps of directly preparing chiral hydroxyl protected D-(-)-tartaric acid through the selective substitution reaction and then hydrolyzing to obtain the product. The reaction conditions of all the steps are easy to operate, the process is simple, and the reaction of each stepis conventional to operate.
Decorated single-enantiomer phosphoramide-based silica/magnetic nanocomposites for direct enantioseparation
Karimi Ahmadabad, Fatemeh,Pourayoubi, Mehrdad,Bakhshi, Hadi
, p. 27147 - 27156 (2019/09/12)
The nano-composites Fe3O4SiO2(-O3Si[(CH2)3NH])P(O)(NH-R(+)CH(CH3)(C6H5))2 (Fe3O4SiO2PTA(+)) and Fe3O4SiO2(-O3Si[(CH2)3NH])P(O)(NH-S(-)CH(CH3)(C6H5))2 (Fe3O4SiO2PTA(-)) were prepared and used for the chiral separation of five racemic mixtures (PTA = phosphoric triamide). The separation results show chiral recognition ability of these materials with respect to racemates belonging to different families of compounds (amine, acid, and amino-acid), which show their feasibility to be potential adsorbents in chiral separation. The nano-composites were characterized by FTIR, TEM, SEM, EDX, XRD, and VSM. The VSM curves of nano-composites indicate their superparamagnetic property, which is stable after their use in the separation process. Fe3O4, Fe3O4SiO2, Fe3O4SiO2PTA(+) and Fe3O4SiO2PTA(-) are regularly spherical with uniform shape and the average sizes of 17-20, 18-23, 36-47 and 43-52 nm, respectively.
Structural insight into the catalytic mechanism of a cis-epoxysuccinate hydrolase producing enantiomerically pure d(-)-tartaric acid
Dong, Sheng,Liu, Xi,Cui, Gu-Zhen,Cui, Qiu,Wang, Xinquan,Feng, Yingang
, p. 8482 - 8485 (2018/08/04)
Crystal structure determination and mutagenesis analysis of a cis-epoxysuccinate hydrolase which produces enantiomerically pure d(-)-tartaric acids revealed a zinc ion and essential residues in the stereoselective mechanism for the catalytic reaction of the small mirror symmetric substrate.