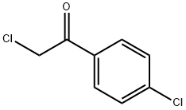
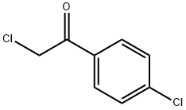
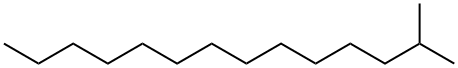
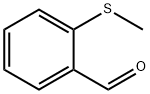
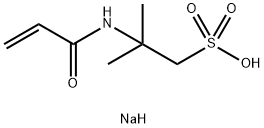
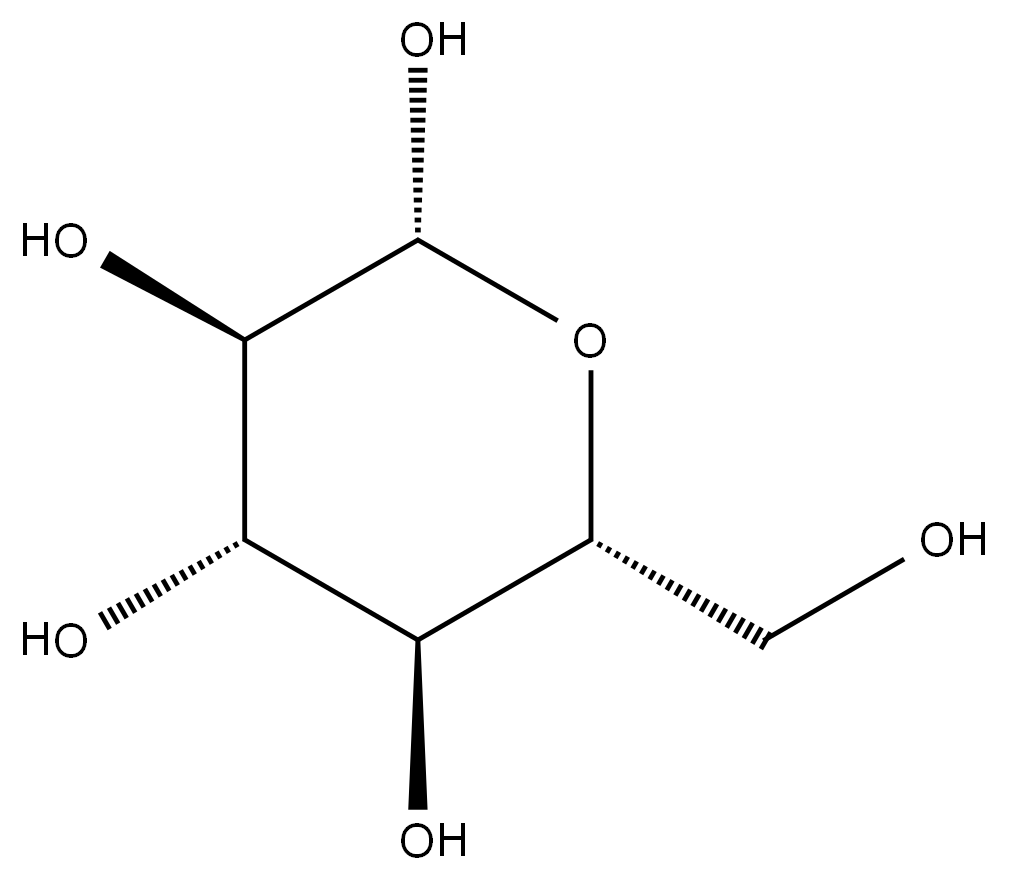
2,4'-Dichloroacetophenone literature
Tris-(2-pyridylmethyl)amine-ligated Cu(II) 1,3-diketonate complexes: Anaerobic retro-Claisen and dehalogenation reactivity of 2-chloro-1,3-diketonate derivatives
Elsberg, Josiah G. D.,Anderson, Stephen N.,Tierney, David L.,Reinheimer, Eric W.,Berreau, Lisa M.
, p. 1712 - 1720 (2021/02/22)
We report synthetic, structural and reactivity investigations of tris-(2-pyridylmethyl)amine (TPA)-ligated Cu(ii) 1,3-diketonate complexes. These complexes exhibit anaerobic retro-Claisen type C-C bond cleavage reactivity which exceeds that found in analo
A practical synthesis of α-bromo/iodo/chloroketones from olefins under visible-light irradiation conditions
Wang, Zhihui,Wang, Lei,Wang, Zhiming,Li, Pinhua,Zhang, Yicheng
supporting information, p. 429 - 432 (2020/02/29)
A practical synthesis of α-bromo/iodo/chloroketones from olefins under visible-light irradiation conditions has been developed. In the presence of PhI(OAc)2 as promoter and under ambient conditions, the reactions of styrenes and triiodomethane undergo the transformation smoothly to deliver the corresponding α-iodoketones without additional photocatalyst in good yields under sunlight irradiation. Meanwhile, the reactions of styrenes with tribromomethane and trichloromethane generate the desired α-bromoketones and α-chloroketones in high yields by using Ru(bpy)3Cl2 as a photocatalyst under blue LED (450–455 nm) irradiation.
Facile Synthesis of α-Haloketones by Aerobic Oxidation of Olefins Using KX as Nonhazardous Halogen Source
Luo, Zhibin,Meng, Yunge,Gong, Xinchi,Wu, Jie,Zhang, Yulan,Ye, Long-Wu,Zhu, Chunyin
supporting information, p. 173 - 177 (2020/01/02)
An operationally simple and safe synthesis of α-haloketones using KBr and KCl as nonhazardous halogen sources is reported. It involves an iron-catalysed reaction of alkenes with KBr/KCl using O2 as terminal oxidant under the irradiation of visible-light. This strategy avoids the risks associated with handling halo-contained electrophiles (Cl2, Br2, NCS, NBS). The process is tolerant to several functional groups, and extended to a range of substituted styrenes in up to 89% yield. A radical reaction pathway is proposed based on control experiments and spectroscopy studies.
A new exploration towards aminothiazolquinolone oximes as potentially multi-targeting antibacterial agents: Design, synthesis and evaluation acting on microbes, DNA, HSA and topoisomerase IV
Wang, Liang-Liang,Battini, Narsaiah,Bheemanaboina, Rammohan R. Yadav,Ansari, Mohammad Fawad,Chen, Jin-Ping,Xie, Yun-Peng,Cai, Gui-Xin,Zhang, Shao-Lin,Zhou, Cheng-He
, p. 166 - 181 (2019/07/02)
This work did a new exploration towards aminothiazolquinolone oximes as potentially multi-targeting antimicrobial agents. A class of novel hybrids of quinolone, aminothiazole, piperazine and oxime fragments were designed for the first time, conveniently synthesized as well as characterized by 1H NMR, 13C NMR and HRMS spectra. Biological activity showed that some of the synthesized compounds exhibited good antimicrobial activities in comparison with the reference drugs. Especially, O-methyl oxime derivative 10b displayed excellent inhibitory efficacy against MRSA and S. aureus 25923 with MIC values of 0.009 and 0.017 mM, respectively. Further studies indicated that the highly active compound 10b showed low toxicity toward BEAS-2B and A549 cell lines and no obvious propensity to trigger the development of bacterial resistance. Quantum chemical studies have also been conducted and rationally explained the structural features essential for activity. The preliminarily mechanism exploration revealed that compound 10b could not only exert efficient membrane permeability by interfering with the integrity of cells, bind with topoisomerase IV–DNA complex through hydrogen bonds and π-π stacking, but also form a steady biosupramolecular complex by intercalating into DNA to exert the efficient antibacterial activity. The supramolecular interaction between compound 10b and human serum albumin (HSA) was a static quenching, and the binding process was spontaneous, where hydrogen bonds and van der Waals force played vital roles in the supramolecular transportation of the active compound 10b by HSA.