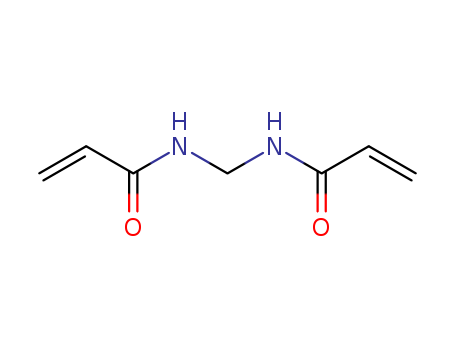
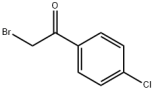
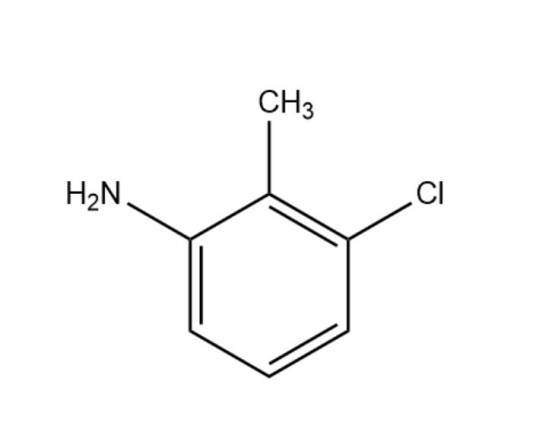
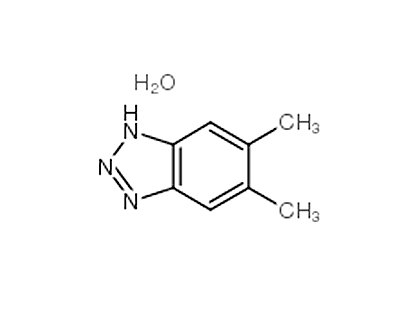
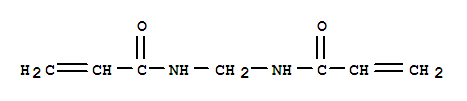N,N'-Methylenebisacrylamide literature
-
Imoto,M. et al.
, p. 1558 - 1560 (1964)
-
Synthesis method of N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide
-
Paragraph 0032-0040, (2021/04/21)
The invention relates to a synthesis method of N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide. With acrylamide and paraformaldehyde as reaction raw materials, N,N'-methylene bisacrylamide is prepared by using a supported heteropolyacid catalyst and an amide activation reagent under the synergistic catalysis. The synergistic use of the supported heteropolyacid catalyst and the amide activation reagent can interact with carbonyl in acrylamide under the condition of not influencing heteropolyacid catalysis, destroy a p-pi conjugated system of amide bonds, improve the nucleophilicity of amino, enhance the reaction activity of amino and paraformaldehyde, and greatly improve the selectivity of the reaction, and therefore, high-efficiency conversion of the raw materials is realized without adding a large amount of water as a reaction solvent, and the reaction yield is improved. With the heteropolyacid catalyst solid-phase load, reaction is conducted on the surface of the solid catalyst, a large amount of acid solvent does not exist in the system, alkali liquor does not need to be added for neutralization in the post-treatment process, post-treatment steps are simplified, and wastewater discharge is reduced.
LAYER SILICATE NANOCOMPOSITES OF POLYMER HYDROGELS AND THEIR USE IN TISSUE EXPANDERS
-
, (2010/10/03)
The invention relates to nanocomposites comprising of (i) hydrogels synthetized by copolymerization of N-isopropylacrylamide and/or acrylamide and/or acrylic acid monomers and of (ii) layer silicates, and to the process for preparing them. The invention covers osmotically active hydrogel expanders containing said nano-composites, suitable for tissue expansion and the use of said materials for obtaining live skin.
MATERIAL FOR METALLIC-PATTERN FORMATION, CROSSLINKING MONOMER, AND METHOD OF FORMING METALLIC PATTERN
-
Page/Page column 17-19, (2008/06/13)
A method of forming a metallic pattern through the chemisorption of a metal; and a pattern-forming material and a crosslinking monomer which are used in the method. The method comprises: a step in which a pattern-forming material having a composition including a matrix polymer (A) having at least either of a carboxy group and a sulfo group is used to form a pattern on a surface of a substrate by a photolithographic technique including the steps of development and rinsing with a pure-water liquid having a pH less than 7; a step in which this pattern is immersed in an aqueous solution containing a metal compound to chemisorb metal ions or metal compound complex ions onto the pattern to form a metal-containing pattern; and a step in which the metal-containing pattern is burned to form a metallic pattern comprising the elemental metal or comprising it and an oxide of the metal. The crosslinking monomer is one comprising a condensate of a polyhydric alcohol with N-methylol(meth)acrylamide.
Microgel particles for the delivery of bioactive materials
-
, (2008/06/13)
Novel microgels, microparticles and related polymeric materials capable of delivering bioactive materials to cells for use as vaccines or therapeutic agents. The materials are made using a crosslinker molecule that contains a linkage cleavable under mild acidic conditions. The crosslinker molecule is exemplified by a bisacryloyl acetal crosslinker. The new materials have the common characteristic of being able to degrade by acid hydrolysis under conditions commonly found within the endosomal or lysosomal compartments of cells thereby releasing their payload within the cell. The materials can also be used for the delivery of therapeutics to the acidic regions of tumors and sites of inflammation.