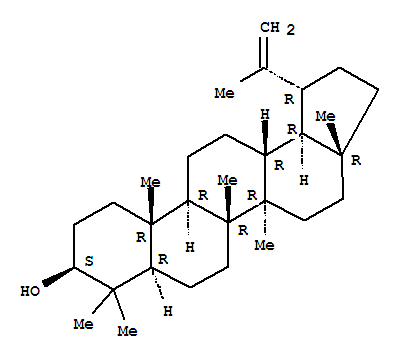
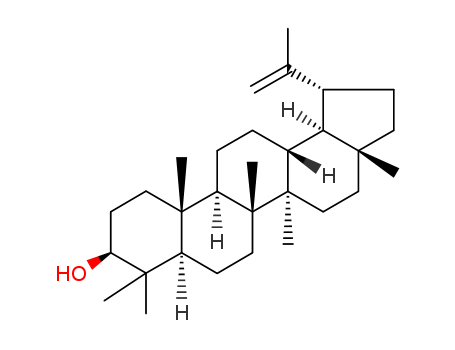
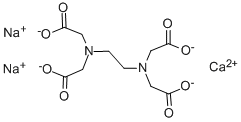
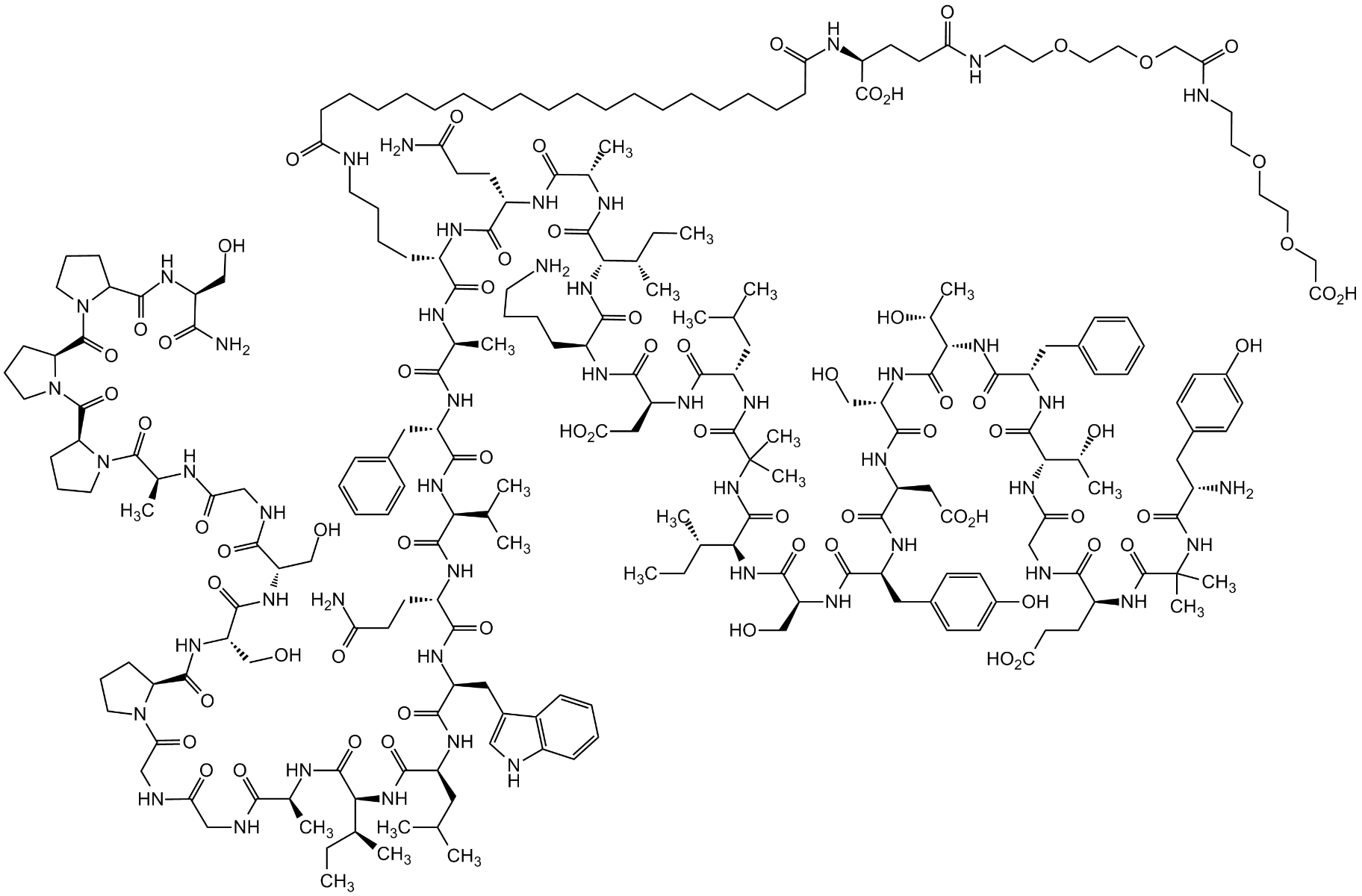
Lupeol literature
Pentacyclic triterpenes and naphthoquinones from Euclea divinorum
Mebe, Paul P.,Cordell, Geoffrey A.,Pezzuto, John M.
, p. 311 - 313 (1998)
Phytochemical studies on Euclea divinorum have resulted in the isolation of lupeol, lupene, betulin, 7-methyljuglone, isodiospyrin, shinalone, catechin and 3β-(5-hydroxyferuloyl)lup-20(30)-ene. The structures were assigned on the basis spectral and chemical studies and the compounds were evaluated for their cytotoxic activity.
TRITERPENOIDS OF AMSONIA GRANDIFLORA
Wahyuono, Subagus,Hoffmann, Joseph J.,Jolad, Shivanand D.,Dentali, Steven J.
, p. 1213 (1987)
Stems and leaves of Amsonia grandiflora yielded lupeol β-hydroxyoctadecanoate, betulinic acid, oleanolic acid, lupeol, lupeol acetate and 1-O-methyl-myo-inositol. - Key Word Index: Amsonia grandiflora; Apocynaceae; stems; leaves; triterpenoids; lupeol β-hydroxyoctadecanoate.
Antibacterial activity of naphthoquinones and triterpenoids from Euclea natalensis root bark
Weigenand, Oliver,Hussein, Ahmed A.,Lall, Namrita,Meyer, Jacobus J. M.
, p. 1936 - 1938 (2004)
Phytochemical studies of an ethanolic extract of Euclea natalensis root bark afforded two new compounds, octahydroeuclein (1) and 20(29)-lupene-3β- isoferulate (2), in addition to three known compounds, shinanolone (3), lupeol, and betulin. The chemical structures of 1 and 2 were determined by spectroscopic means. Shinanolone (3) showed inhibitory activity against Gram-positive bacterial strains and a drug-sensitive strain of Mycobacterium tuberculosis at a concentration of 0.1 mg/mL.
Synthesis of Lupeol from Betulin
Garifullina,Myasoedova, Yu. V.,Ishmuratova
, p. 765 - 767 (2019/08/07)
-
Practical Synthesis of α-Amyrin, β-Amyrin, and Lupeol: The Potential Natural Inhibitors of Human Oxidosqualene Cyclase
Chen, Dongyin,Xu, Fengguo,Zhang, Pu,Deng, Jie,Sun, Hongbin,Wen, Xiaoan,Liu, Jun
, (2017/10/20)
A practical synthesis of α-amyrin (1), β-amyrin (2), and lupeol (3) was accomplished in total yields of 32, 42, and 40% starting from easily available ursolic acid (4), oleanolic acid (5), and betulin (6), respectively. Remarkably, these three natural pentacyclic triterpenes exhibited potential inhibitory activity against human oxidosqualene cyclase.
And reclaims to clean rough synthesis method
-
Paragraph 0036-0041; 0053-0055, (2017/08/25)
The invention belongs to the research field of bioactive substance preparation processes, and provides a synthesis method of lupeol. The lupeol is prepared by reduction reaction in the presence of a reducer and strong alkaline by taking betulinaldehyde or a 3-ester derivative thereof as raw materials. The method is less in experimental steps, simple to operate and high in yield, and the production cost of the lupeol is remarkably reduced.
Lupeol-3-O-decanoate, a new triterpene ester from Cadaba farinosa Forssk. growing in Saudi Arabia
Al-Musayeib, Nawal M.,Mohamed, Gamal A.,Ibrahim, Sabrin R. M.,Ross, Samir A.
, p. 5297 - 5302 (2013/12/04)
A new triterpene ester (1) together with eight known compounds (2-9) were isolated from the leaves of Cadaba farinosa Forssk. Their chemical structures were established on the basis of physical, chemical, and spectroscopic methods (IR, 1D and 2D NMR, and mass spectral analyses) to be: lupeol-3-O-decanoate (1), lupeol (2), β-sitosterol (3), ursolic acid (4), 12-aminododecanoic (5), dillenetin-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (6), stachydrine (7), 3-hydroxy-stachydrine (8), and quercetin-3-O-β-d-glucopyranoside (9). That is the first report for the isolation of compound 5 from a plant source. Compounds 5, 6, and 9 were evaluated for their antioxidant activity.