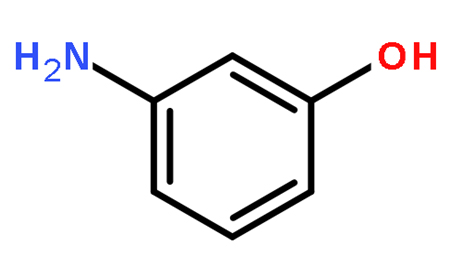
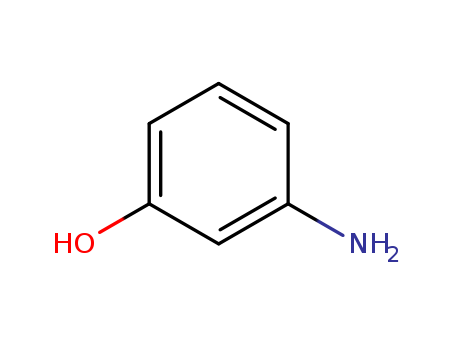
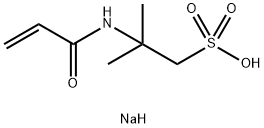
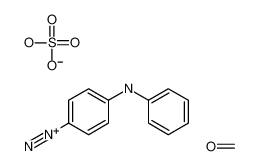
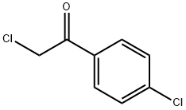
3-Aminophenol literature
Preparation of resorcinarene-functionalized gold nanoparticles and their catalytic activities for reduction of aromatic nitro compounds
Yao, Yong,Sun, Yan,Han, Ying,Yan, Chaoguo
, p. 705 - 712 (2010)
Resorcinarene-functionalized gold nanoparticles (AuNPs) were prepared conveniently in aqueous solution in the presence of amphiphilic tetramethoxyresorcinarene tetraaminoamide. The obtained AuNPs were characterized and analyzed by UV-vis, FT-IR, XRD and TEM, respectively. The results showed that the size of AuNPs and the standard deviations were all decreasing with the increase of resorcinarene concentration. In addition, the catalytic activity of the obtained AuNPs in the reduction of aromatic nitro compounds was also investigated. In aqueous solution the reaction follows a first order kinetics and the size of AuNPs has influence on the rate of reduction.
Effects of grinding with or without microcrystalline cellulose on the decomposition of p-aminosalicylic acid
Nakai,Nakajima,Yamamoto,et al.
, p. 734 - 738 (1982)
-
Pd nanoparticles supported on cubic shaped ZIF-based materials and their catalytic activates in organic reactions
Dabiri, Minoo,Fazli, Hassan,Movahed, Siyavash Kazemi,Salarinejad, Neda
, (2021)
Pd nanoparticles decorated on cubic shaped ZIF-based materials have been successfully prepared. The nanocomposites have been characterized by X-ray diffraction, field emission scanning electron microscopy, N2 sorption analysis, and transmission
Freeze-drying of drug-additive binary systems. II. relationship between decarboxylation behavior and molecular states of p-Aminosalicylic acid
Oguchi,Yonemochi,Yamamoto,Nakai
, p. 3088 - 3091 (1989)
-
Ag-NPs embedded in two novel Zn3/Zn5-cluster-based metal-organic frameworks for catalytic reduction of 2/3/4-nitrophenol
Wu, Xue-Qian,Huang, Dan-Dan,Zhou, Zhi-Hang,Dong, Wen-Wen,Wu, Ya-Pan,Zhao, Jun,Li, Dong-Sheng,Zhang, Qichun,Bu, Xianhui
, p. 2430 - 2438 (2017)
By utilizing symmetrical pentacarboxylate ligands, 3,5-di(2′,5′-dicarboxylphenyl)benzoic acid (H5L1) and 3,5-di(2′,4′-dicarboxylphenyl)benzoic acid (H5L2), two novel porous Zn-MOFs, [Zn5(μ3-H2O)2(L1)2]·3DMA·4H2O (CTGU-3) and [Zn3(μ3-OH)L2(H2O)3]·H2O (CTGU-4) have been synthesized under solvothermal conditions. CTGU-3 and CTGU-4 exhibit 3D microporous frameworks with flu and dia topologies and possess unique secondary building units [Zn5(μ3-H2O)2(RCO2)6] and [Zn3(μ3-OH)(RCO2)3], respectively. Such porous systems create a unique space or surface to accommodate Ag nanoparticles (Ag NPs), which could efficiently prevent Ag NPs from aggregation and leaching. In this work, two new Ag@Zn-MOF composites, denoted as Ag@CTGU, have been successfully fabricated through solution infiltration, for the reduction of nitrophenol. Compared with CTGU-4, CTGU-3 shows enhanced catalytic efficiency toward the reaction when it is used as a catalyst support of Ag NPs. Moreover, gas sorption and luminescence properties of two compounds were also investigated.
Tubular Structures Self-Assembled from a Bola-Amphiphilic Pillar[5]arene in Water and Applied as a Microreactor
Chen, Rener,Jiang, Huajiang,Gu, Haining,Zhou, Qizhong,Zhang, Zhen,Wu, Jiashou,Jin, Zhengneng
, p. 4160 - 4163 (2015)
Various nanomorphologies were obtained by simply changing the fabrication conditions, such as the pH of the system, different solvent, or different concentration, of bola-amphiphilic pillar[5]arene Bola-AP5. Importantly, hybrid microtubules as a microreac
Nickel Boride Catalyzed Reductions of Nitro Compounds and Azides: Nanocellulose-Supported Catalysts in Tandem Reactions
Proietti, Giampiero,Prathap, Kaniraj Jeya,Ye, Xinchen,Olsson, Richard T.,Dinér, Peter
, p. 133 - 146 (2021/11/04)
Nickel boride catalyst prepared in situ from NiCl2 and sodium borohydride allowed, in the presence of an aqueous solution of TEMPO-oxidized nanocellulose (0.01 wt%), the reduction of a wide range of nitroarenes and aliphatic nitro compounds. Here we describe how the modified nanocellulose has a stabilizing effect on the catalyst that enables low loading of the nickel salt pre-catalyst. Ni-B prepared in situ from a methanolic solution was also used to develop a greener and facile reduction of organic azides, offering a substantially lowered catalyst loading with respect to reported methods in the literature. Both aromatic and aliphatic azides were reduced, and the protocol is compatible with a one-pot Boc-protection of the obtained amine yielding the corresponding carbamates. Finally, bacterial crystalline nanocellulose was chosen as a support for the Ni-B catalyst to allow an easy recovery step of the catalyst and its recyclability for new reduction cycles.
Selective hydrodeoxygenation of acetophenone derivatives using a Fe25Ru75@SILP catalyst: a practical approach to the synthesis of alkyl phenols and anilines
Bordet, Alexis,Goclik, Lisa,Leitner, Walter,Walschus, Henrik
supporting information, p. 2937 - 2945 (2022/04/07)
A versatile synthetic pathway for the production of valuable alkyl phenols and anilines has been developed based on the selective hydrodeoxygenation of a wide range of hydroxy-, amino-, and nitro-acetophenone derivatives as readily available substrates. Bimetallic iron ruthenium nanoparticles immobilized on an imidazolium-based supported ionic liquid phase (Fe25Ru75@SILP) act as highly active and selective catalysts for the deoxygenation of the side-chain without hydrogenation of the aromatic ring. The catalytic system allows operation under continuous flow conditions with high robustness and flexibility as demonstrated for the alternating conversion of 3′,5′-dimethoxy-4′-hydroxyacetophenone and 4′-hydroxynonanophenone as model substrates.
Surface Roughness Effects of Pd-loaded Magnetic Microspheres on Reduction Kinetics of Nitroaromatics
An, Seonghwi,Manivannan, Shanmugam,Viji, Mayavan,Shim, Min Suk,Hwang, Byeong Hee,Kim, Kyuwon
supporting information, p. 894 - 899 (2021/05/06)
Metal nanoparticles decoration on magnetically active semiconductor materials is a common strategy to improve the colloidal stability, catalyst harvesting, and reuse. In this study, a surfactant-free solvothermal method followed by a heat treatment to pre