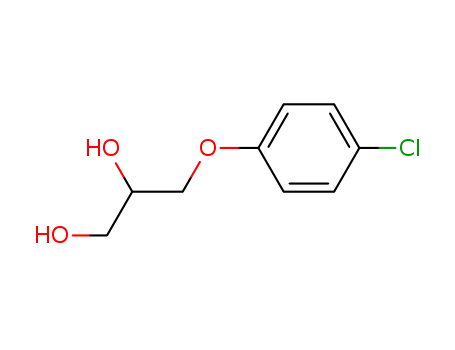
Chlorphenesin literature
A New and Efficient Heterogeneous System for the Oxidative Cleavage of 1,2-Diols and the Oxidation of Hydroquinones
Daumas, M.,Vo-Quang, Y.,Vo-Quang, L.,Goffic, F. Le
, p. 64 - 65 (1989)
Sodium periodate/wet silica gel in the presence of dichloromethane is an efficient reagent for the oxidative cleavage of 1,2-diols and the oxidation of hydroquinones.This easily prepared reagent provides a good alternative of classical metaperiodate oxidation, especially for the preparation of aldehydes, which easily form hydrates.
One-pot synthesis of aryloxypropanediols from glycerol: Towards valuable chemicals from renewable sources
Truscello, Ada M.,Gambarotti, Cristian,Lauria, Mirvana,Auricchio, Sergio,Leonardi, Gabriella,Shisodia, Suresh U.,Citterio, Attilio
, p. 625 - 628 (2013)
Glycerol offers an easy and green route for the synthesis of aryloxypropanediols of known pharmacological activity. Glycerol is selectively converted to aryloxypropanediols in a one-pot reaction, through in situ formed glycerol carbonate, under benign and solvent-free conditions. Catalyst and unreacted reagent can be recycled.
Kinetics and mechanism of degradation of chlorphenesin carbamate in strongly acidic aqueous solutions
Hara,Hayashi,Yoshida
, p. 3481 - 3484 (1986)
-
Ligand-Free Copper-Catalyzed Ullmann-Type C?O Bond Formation in Non-Innocent Deep Eutectic Solvents under Aerobic Conditions
Capriati, Vito,García-álvarez, Joaquín,Marinò, Manuela,Perna, Filippo M.,Quivelli, Andrea Francesca,Vitale, Paola
, (2021/12/09)
An efficient and novel protocol was developed for a Cu-catalyzed Ullmann-type aryl alkyl ether synthesis by reacting various (hetero)aryl halides (Cl, Br, I) with alcohols as active components of environmentally benign choline chloride-based eutectic mixtures. Under optimized conditions, the reaction proceeded under mild conditions (80 °C) in air, in the absence of additional ligands, with a catalyst [CuI or CuII species] loading up to 5 mol% and K2CO3 as the base, providing the desired aryloxy derivatives in up to 98 % yield. The potential application of the methodology was demonstrated in the valorization of cheap, easily available, and naturally occurring polyols (e. g., glycerol) for the synthesis of some pharmacologically active aryloxypropanediols (Guaiphenesin, Mephenesin, and Chlorphenesin) on a 2 g scale in 70–96 % yield. Catalyst, base, and deep eutectic solvent could easily and successfully be recycled up to seven times with an E-factor as low as 5.76.
Exploration of the expeditious potential of Pseudomonas fluorescens lipase in the kinetic resolution of racemic intermediates and its validation through molecular docking
Soni, Surbhi,Dwivedee, Bharat P.,Sharma, Vishnu K.,Patel, Gopal,Banerjee, Uttam C.
, p. 85 - 94 (2017/12/26)
A profoundly time-efficient chemoenzymatic method for the synthesis of (S)-3-(4-chlorophenoxy)propan-1,2-diol and (S)-1-chloro-3-(2,5-dichlorophenoxy)propan-2-ol, two important pharmaceutical intermediates, was successfully developed using Pseudomonas fluorescens lipase (PFL). Kinetic resolution was successfully achieved using vinyl acetate as acylating agent, toluene/hexane as solvent, and reaction temperature of 30°C giving high enantioselectivity and conversion. Under optimized condition, PFL demonstrated 50.2% conversion, enantiomeric excess of 95.0%, enantioselectivity (E?=?153) in an optimum time of 1?hour and 50.3% conversion, enantiomeric excess of 95.2%, enantioselectivity (E?=?161) in an optimum time of 3?hours, for the two racemic alcohols, respectively. Docking of the R- and S-enantiomers of the intermediates demonstrated stronger H-bond interaction between the hydroxyl group of the R-enantiomer and the key binding residues of the catalytic site of the lipase, while the S-enantiomer demonstrated lesser interaction. Thus, docking study complemented the experimental outcome that PFL preferentially acylated the R form of the intermediates. The present study demonstrates a cost-effective and expeditious biocatalytic process that can be applied in the enantiopure synthesis of pharmaceutical intermediates and drugs.
Method for green, efficient and selective synthesis of chlorphenesin
-
Paragraph 0028-0043, (2018/09/13)
The invention discloses a method for green, efficient and selective synthesis of chlorphenesin. Glycerol and 4-chlorophenol directly serve as raw materials, diethyl carbonate serves as a selective synthesis agent, separate synthesis can be performed in situ, orientation reaction is ensured, other by-products are omitted, separation and purification are simple, yield is 95% under proper conditions,and purity is 99.5% or more. The yield of the chlorphenesin is greatly improved, high-toxic and expensive 3-chlorine-1, 2-propanediol is abandoned by the aid of low-cost and non-toxic glycerin, reaction conditions are mild, and industrial production is facilitated.
A synthesis method of chlorphenesin
-
Paragraph 0082; 0083, (2017/09/01)
The invention relates to a synthetic method of chlorobenzene glyceryl ether. 3-chloro-1,2-propanediol and parachlorophenol are directly used as raw materials, high-corrosion chemical solvents are not introduced, a reaction is simple, the yield is high, and the yield can reach 95 percent or more under the optimal reaction condition. By adding a few phase transfer catalysts, the reaction can be promoted to be conducted quickly and effectively, and the reaction time can be shortened by at least two hours.