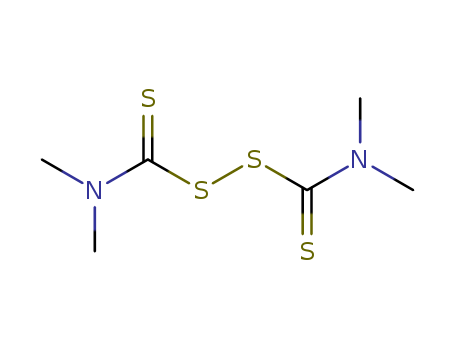
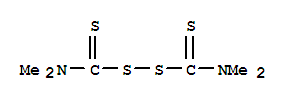Tetramethylthiuram Disulfide literature
Trimethylchlorosilane (TMSCl) and cyanuric chloride (CC) catalyzed efficient oxidative coupling of thiols with dimethylsulfoxide
Karimi, Babak,Hazarkhani, Hassan,Zareyee, Daryoush
, p. 2513 - 2516 (2002)
Different types of thiols were rapidly and efficiently converted to disulfides using DMSO in the presence of catalytic amounts of either trimethylchlorosilane (TMSCl) or cyanuric chloride (CC).
Development of an improved method for conversion of thiuram disulfides into N,N-dialkylcarbamoyl halides and derivatives
Adeppa,Rupainwar,Misra, Krishna
, p. 285 - 290 (2011)
A convenient procedure for preparing N,N-disubstituted carbamoyl halides is reported. It consists of two steps: (1) reaction of carbon disulfide and a secondary amine in the presence of a polar organic solvent and oxygen to produce the corresponding tetraalkyl thiuram disulfides and (2) reaction of tetraalkyl thiuram disulfide with a halide in the presence of an aprotic organic solvent to produce the corresponding N,N-disubstituted carbamoyl halide. Copyright Taylor & Francis Group, LLC.
Carbonic anhydrase inhibitors: Sulfonamides as antitumor agents?
Supuran, Claudiu T,Briganti, Fabrizio,Tilli, Silvia,Chegwidden,Scozzafava, Andrea
, p. 703 - 714 (2001)
Novel sulfonamide inhibitors of the zinc enzyme carbonic anhydrase CA, EC 4.2.1.1) were prepared by reaction of aromatic or heterocyclic sulfonamides containing amino, imino, or hydrazino moieties with N,N-dialkyldithiocarbamates in the presence of oxidiz
Zinc(II)-catalyzed disproportionation in rubber: The mechanism of sulfur vulcanization revisited
Nieuwenhuizen, Peter J.,Timal, Sandjai,Haasnoot, Jaap G.,Spek, Anthony L.,Reedijk, Jan
, p. 1846 - 1851 (1997)
Model studies have shown that cross-link precursors, that is, intermediates in the sulfur vulcanization of rubber, are transformed into cross-links by a nonsymmetric but regioselective disproportionation mechanism. Thus, two equivalents of the cross-link precursor of the type R-S-S-X are transformed into X-S-X and the actual cross-link R-S-S-S-R. Exchange of sulfur atoms is a prerequisite. A mechanism involving an S(N)i' reaction with an allylic moiety, suggested in the literature, has not been observed. The disproportionation reaction is catalyzed by rubber-soluble zinc-dithio-carbamate complexes, an important class of vulcanization accelerators. By virtue of ligand-functional-group exchange reactions these complexes serve to transport and exchange sulfur atoms.
Microfluidic electrosynthesis of thiuram disulfides
Zheng, Siyuan,Wang, Kai,Luo, Guangsheng
, p. 582 - 591 (2021)
An electrolytic approach to sodium dithiocarbamates based on a microfluidic reactor is proposed for the green synthesis of thiuram disulfides, which are versatile free radical initiators. The electro-oxidation reactions avoid the over-oxidation of sodium dithiocarbamates and the generation of waste salts, which have perplexed the industry for a long time. This microfluidic electrolysis method prevents solid deposition by introducing liquid-liquid Taylor flow into the microchannel, and promotes the synthesis efficiency of thiuram disulfides with the enlargement of the electrode-specific surface area. The highest yield of thiuram disulfide was 88% in the experiment without any oxidation by-products. The Faraday efficiencies of most reactions are higher than 96%, showing the excellent electronic utilization. In addition to improving the environmental friendliness of sodium dithiocarbamate oxidation, the electrosynthesis method helps to create a cyclic technology of thiuram disulfide synthesis via the combination of sodium dithiocarbamate generation in a packed bed reactor. The cyclic technology finally achieved >99% atom utilization in thiuram disulfide synthesis from secondary amines and carbon disulfide. This journal is
Method for preparing tetraalkyl thiuram disulfide through photocatalytic oxidation
-
Paragraph 0061-0064, (2021/02/13)
The invention relates to a method for preparing tetraalkyl thiuram disulfide by photocatalytic oxidation. The method comprises the following steps: carrying out mixed reaction on secondary amine, carbon disulfide and a catalyst in a medium to generate an intermediate product; and carrying out catalytic oxidation reaction on the intermediate product under illumination to obtain tetraalkyl thiuram disulfide. According to the invention, the method is high in reaction speed and mild in condition, and energy conservation and efficiency improvement are achieved; the used medium and catalyst can be recycled, so that the resource utilization rate is improved; and the method does not produce inorganic salt by-products, and the product has high yield and high purity.
Continuous-flow step-economical synthesis of thiuram disulfidesviavisible-light photocatalytic aerobic oxidation
Xu, Hao-Xing,Zhao, Ze-Run,Patehebieke, Yeersen,Chen, Qian-Qian,Fu, Shun-Guo,Chang, Shuai-Jun,Zhang, Xu-Xu,Zhang, Zhi-Liang,Wang, Xiao
supporting information, p. 1280 - 1285 (2021/02/26)
A continuous-flow photocatalytic synthesis of the industrially important thiuram disulfides has been developed, utilizing O2as the oxidant and Eosin Y as the photoredox catalyst. This highly atom- and step-economical method features much reduced reaction time as well as excellent product yield and purity, making it a sustainable and potentially scalable process for industrial production.
Development of disulfide-derived fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase) covalent inhibitors for the treatment of type 2 diabetes
Xu, Yi-xiang,Huang, Yun-yuan,Song, Rong-rong,Ren, Yan-liang,Chen, Xin,Zhang, Chao,Mao, Fei,Li, Xiao-kang,Zhu, Jin,Ni, Shuai-shuai,Wan, Jian,Li, Jian
, (2020/07/25)
Fructose-1,6-bisphosphatase (FBPase), as a key rate-limiting enzyme in the gluconeogenesis (GNG) pathway, represents a practical therapeutic strategy for type 2 diabetes (T2D). Our previous work first identified cysteine residue 128 (C128) was an important allosteric site in the structure of FBPase, while pharmacologically targeting C128 attenuated the catalytic ability of FBPase. Herein, ten approved cysteine covalent drugs were selected for exploring FBPase inhibitory activities, and the alcohol deterrent disulfiram displayed superior inhibitory efficacy among those drugs. Based on the structure of lead compound disulfiram, 58 disulfide-derived compounds were designed and synthesized for investigating FBPase inhibitory activities. Optimal compound 3a exhibited significant FBPase inhibition and glucose-lowering efficacy in vitro and in vivo. Furthermore, 3a covalently modified the C128 site, and then regulated the N125–S124–S123 allosteric pathway of FBPase in mechanism. In summary, 3a has the potential to be a novel FBPase inhibitor for T2D therapy.