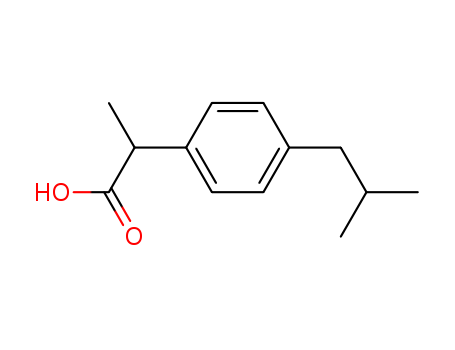
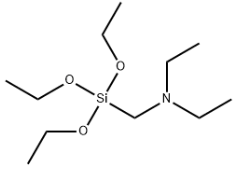
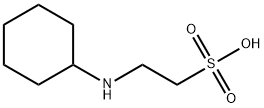
Ibuprofen literature
A NOVEL SYNTHESIS OF α,β-UNSATURATED NITRILES FROM AROMATIC KETONES VIA CYANOPHOSPHATES
Harusawa, Shinya,Yoneda, Ryuji,Kurihara, Takushi,Hamada, Yasumasa,Shioiri, Takayuki
, p. 427 - 428 (1984)
Reaction of aromatic ketones with diethyl phosphorocyanidate in the presence of lithium cyanide gave cyanophosphates, which were converted into α,β-unsaturated nitriles by treatment with boron trifluoride etherate in high yields.
Synthesis, pharmacological activity and hydrolytic behavior of glyceride prodrugs of ibuprofen
Khan,Akhter, Mymoona
, p. 371 - 376 (2005)
For reducing the gastrointestinal toxicity associated with ibuprofen its carboxylic group was condensed with the hydroxyl group of 1,2,3-trihydroxy propane 1,3-dipalmitate/stearate to give the ester prodrugs 3a and 3b. The release of ibuprofen from these prodrugs has been studied at pH 3, 4, 5 and 7.4 by HPLC using methanol and 0.05% phosphoric acid (80%) (70:30) as mobile phase. The prodrugs showed insignificant hydrolysis at pH 5 compared to pH 7.4 indicating that the prodrugs do not break in stomach but release ibuprofen at pH 7.4 in adequate amounts. In vivo hydrolysis studies in rats, the peak plasma concentration of ibuprofen was attained in 1.5:h in case of ibuprofen and in 2:h in prodrugs treated animals. The plasma concentration was found to be less at all times in animals treated with ibuprofen compared to the prodrugs treated animals. The maximum anti-inflammatory activity of ibuprofen was observed at 2 h whereas prodrugs showed maximum activity at 3 h and remained practically constant upto 8:h whereas a decrease in activity was observed with free ibuprofen. Further the prodrugs showed less gastric ulcers compared to ibuprofen. An average score of 0.16, 0.45, 0.97 and 0.20, 0.76, 1.02 of ulcers was observed with 3a and 3b compared to an average score of 0.75, 1.10, and 2.97 with ibuprofen. These prodrugs also showed significant protection against acetic acid induced writhings in rats. These finding suggested that both the prodrugs are better in action as compared to the parent drug and are advantageous in having less gastrointestinal side effects.
The continuous-flow synthesis of ibuprofen
Bogdan, Andrew R.,Poe, Sarah L.,Kubis, Daniel C.,Broadwater, Steven J.,McQuade, D. Tyler
, p. 8547 - 8550 (2009)
Let relief flow forth I A three-step, continuous-flow synthesis of ibuprofen was accomplished using a simplified microreactor. By designing a synthesis in which excess reagents and byproducts are compatible with downstream reactions, no intermediate purification or isolation steps are required.
Nickel-Catalyzed Markovnikov Addition of Hydrogen Cyanide to Olefins. Application to Nonsteroidal Antiinflammatories
Nugent, William A.,McKinney, Ronald J.
, p. 5370 - 5372 (1985)
-
-
Walker,Pillai
, p. 3707 (1977)
-
The digital code driven autonomous synthesis of ibuprofen automated in a 3D-printer-based robot
Kitson, Philip J.,Glatzel, Stefan,Cronin, Leroy
, p. 2776 - 2783 (2016)
An automated synthesis robot was constructed by modifying an open source 3D printing platform. The resulting automated system was used to 3D print reaction vessels (reactionware) of differing internal volumes using polypropylene feedstock via a fused deposition modeling 3D printing approach and subsequently make use of these fabricated vessels to synthesize the nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drug ibuprofen via a consecutive one-pot three-step approach. The synthesis of ibuprofen could be achieved on different scales simply by adjusting the parameters in the robot control software. The software for controlling the synthesis robot was written in the python programming language and hard-coded for the synthesis of ibuprofen by the method described, opening possibilities for the sharing of validated synthetic 'programs' which can run on similar low cost, user-constructed robotic platforms towards an 'open-source' regime in the area of chemical synthesis.
Highly active supported palladium catalyst for the regioselective synthesis of 2-arylpropionic acids by carbonylation
Jayasree,Seayad,Chaudhari
, p. 1067 - 1068 (1999)
A catalyst system consisting of supported palladium in the presence of phosphine ligands, TsOH and LiCl catalyses the carbonylation of 1-arylethanols to 2-arylpropionic acids with significantly improved activity and regioselectivity; the catalyst can be recycled with no loss in activity and selectivity.
One-step synthesis of methyl 2-arylpropanoates from 2-hydroxypropiophenone dimethylacetals using sulfuryl chloride and an amide or a weak base
Yamauchi,Hattori,Nakao,Tamaki
, p. 1044 - 1045 (1986)
-
Synthesis of Methyl 2-Arylpropanoates by 1,2-Aryl Migration of Aryl Ethyl Ketones using Diacetoxyphenyliodine
Tamura, Yasumitsu,Shirouchi, Yoshiaki,Haruta, Jun-ichi
, p. 231 - 232 (1984)
-
Synthesis and hydrolytic behaviour of glycerol-1,2-diibuprofenate-3-nitrate, a putative pro-drug of ibuprofen and glycerol-1-nitrate
Ingram,Moynihan,Powell,Rostron
, p. 345 - 350 (2001)
Nitroxylated derivatives of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs appear to offer protection against the gastrotoxicity normally associated with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, ostensibly via local production of nitric oxide. A diester of ibuprofen and glycerol-1-mononitrate has been prepared via the condensation of ibuprofen with 3-bromopropan-1,2-diol, followed by silver-(I)-nitrate-mediated nitroxylation. The release of ibuprofen from this diester has been studied in a simulated gastric fluid model with direct analysis by reverse-phase HPLC, using an acetonitrile-water (80 % :20 %) mobile phase containing trifluoroacetic acid (0.005%). n-Propyl ibuprofen was found to undergo pH-dependent hydrolysis, ranging from negligible hydrolysis at pH 5 to 52 % hydrolysis at pH 3, over a 2-h period in this model. The ibuprofen-glycerol mononitrate diester was subjected to the most vigorous model hydrolytic conditions and was found to undergo 50 % hydrolysis during the study period. This study shows that pro-drugs of ibuprofen and glycerol mononitrate can be obtained, and can undergo degradation to the parent drugs under conditions simulating those likely to be encountered in the stomach.
Carbonylation of vinyl aromatics: Convenient regioselective synthesis of 2-arylpropanoic acids
Seayad,Jayasree,Chaudhari
, p. 459 - 461 (1999)
(equation presented) Various substituted and nonsubstituted 2-arylpropanoic acids have been synthesized in high turnovers with high regioselectivity by palladium-catalyzed carbonylation of vinyl aromatics. Both terminal and internal olefins are carbonylated, though hindered olefins are less reactive. In all the cases high yields and high selectivity are observed. Olefins with electron-withdrawing para substituents gave the highest regioselectivity in the formation of the corresponding 2-arylpropanoic acids.
Separate mechanisms of ion oligomerization tune the physicochemical properties of n-butylammonium acetate: Cation-base clusters vs. Anion-acid dimers
Berton, Paula,Kelley, Steven P.,Wang, Hui,Myerson, Allan S.,Rogers, Robin D.
, p. 25544 - 25554 (2017)
We investigated the ability of the ions comprising protic ionic liquids to strongly interact with their neutral acid and base forms through the characterization of n-butylammonium acetate ([C4NH3][OAc]) in the presence of excess n-butylamine (C4NH2) or excess acetic acid (HOAc). The conjugate and parent acid or base form new nonstoichiometric, noncovalently bound species (i.e., oligomeric ions) which change the physical and chemical properties of the resulting liquids, thus offering tunability. The effects of adding C4NH2 or HOAc to [C4NH3][OAc] on the resulting thermal and spectroscopic properties differ and suggest that C4NH2 interacts primarily with [C4NH3]+ to form 3-dimensional polymeric networks likely similar to those in H2O/[H3O]+, while HOAc interacts primarily with [OAc]- to form oligomeric ions (e.g., [H(OAc)2]-). The densities of the systems increased with the increase of acid content and reached a maximum when the acid molar fraction was 0.90, but decreased with increasing amine concentration. The viscosities decreased significantly with increasing acid or base concentration. The solvent properties of the mixtures were assessed by measuring the solubilities of benzene, ethyl acetate, diethyl ether, heptane, ibuprofen free acid, and lidocaine free base. The solubilities of the organic solutes and active pharmaceutical ingredients can be tuned with the concentration of acid or amine in the mixtures. In addition, crystallization of the active pharmaceutical ingredients can be induced with the modification of the composition of the mixtures. These observations support the usage of these mixtures for the synthesis and purification of acid or basic active pharmaceutical ingredients in the pharmaceutical industry.
Thermal decomposition of ibuproxam
Chimichi,Innocenti,Orzalesi
, p. 521 - 523 (1980)
-
-
White,D.R.,Wu,D.K.
, p. 988 - 989 (1974)
-
-
Shiori,Kawai
, p. 2936 (1978)
-
NMR spectroscopic studies on the in vitro acyl glucuronide migration kinetics of ibuprofen ((±)-(R,S)-2-(4-isobutylphenyl) propanoic acid), its metabolites, and analogues
Johnson, Caroline H.,Wilson, Ian D.,Harding, John R.,Stachulski, Andrew V.,Iddon, Lisa,Nicholson, Jeremy K.,Lindon, John C.
, p. 8720 - 8727 (2007)
Carboxylic acid-containing drugs are often metabolized to 1-β-O-acyl glucuronides (AGs). These can undergo an internal chemical rearrangement, and the resulting reactive positional isomers can bind to endogenous proteins, with clear potential for adverse effects. Additionally any 1-β-O-acyl- glucuronidated phase I metabolite of the drug can also show this propensity, and investigation of the adverse effect potential of a drug also needs to consider such metabolites. Here the transacylation of the common drug ibuprofen and two of its metabolites is investigated in vitro. 1-β-O-Acyl (S)-ibuprofen glucuronide was isolated from human urine and also synthesized by selective acylation. Urine was also used as a source of the (R)-ibuprofen, (S)-2-hydroxyibuprofen, and (S,S)-carboxy-ibuprofen AGs. The degradation rates (a combination of transacylation and hydrolysis) were measured using 1H NMR spectroscopy, and the measured decrease in the 1-β anomer over time was used to derive half-lives for the glucuronides. The biosynthetic and chemically synthesized (S)-ibuprofen AGs had half-lives of 3.68 and 3.76 h, respectively. (R)-Ibuprofen AG had a half-life of 1.79 h, a value approximately half that of the (S)-diastereoisomer, consistent with results from other 2-aryl propionic acid drug AGs. The 2-hydroxyibuprofen and carboxyibuprofen AGs gave half-lives of 5.03 and 4.80 h, considerably longer than that of either of the parent drug glucuronides. In addition, two (S)-ibuprofen glucuronides were synthesized with the glucuronide carboxyl function esterified with either ethyl or allyl groups. The (S)-ibuprofen AG ethyl ester and (S)-ibuprofen AG allyl esters were determined to have half-lives of 7.24 and 9.35 h, respectively. In order to construct useful structure-reactivity relationships, it is necessary to evaluate transacylation and hydrolysis separately, and here it is shown that the (R)- and (S)-ibuprofen AGs have different transacylation properties. The implications of these findings are discussed in terms of structure-activity relationships.
Expanding the substrate scope of enzymes: Combining mutations obtained by CASTing
Reetz, Manfred T.,Carballeira, Jose Daniel,Peyralans, Jerome,Hoebenreich, Horst,Maichele, Andrea,Vogel, Andreas
, p. 6031 - 6038 (2006)
In a previous paper, the combinatorial active-site saturation test (CAST) was introduced as an effective strategy for the directed evolution of enzymes toward broader substrate acceptance. CASTing comprises the systematic design and screening of focused libraries around the complete binding pocket, but it is only the first step of an evolutionary process because only the initial libraries of mutants are considered. In the present study, a simple method is presented for further optimization of initial hits by combining the mutational changes obtained from two different libraries. Combined lipase mutants were screened for hydrolytic activity against six notoriously difficult substrates (bulky carboxylic acid esters) and improved mutants showing significantly higher activity were identified. The enantioselectivity of the mutants in the hydrolytic kinetic resolution of two substrates was also studied, with the best mutant-substrate combination resulting in a selectivity factor of E=49. Finally, the catalytic profile of the evolved mutants in the hydrolysis of simple nonbranched carboxylic acid esters, ranging from acetate to palmitate, was studied for theoretical reasons.
Room-temperature Pd-catalyzed methoxycarbonylation of terminal alkynes with high branched selectivity enabled by bisphosphine-picolinamide ligand
Chen, Fen-Er,Ke, Miaolin,Liu, Ding,Ning, Yingtang,Ru, Tong
, p. 1041 - 1044 (2022/01/28)
We report the room-temperature Pd-catalyzed methoxy-carbonylation with high branched selectivity using a new class of bisphosphine-picolinamide ligands. Systematic optimization of ligand structures and reaction conditions revealed the significance of both
The total synthesis of (-) -strempeliopine: Via palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative asymmetric allylic alkylation
An, Yi,Chen, Fener,Li, Weijian,Li, Yaling,Tang, Pei,Wang, Zhenzhen,Wu, Mengjuan,Xue, Yansong
, p. 1402 - 1405 (2022/02/09)
In the work reported herein, the concise and enantioselective total synthesis of the Schizozygine alkaloid (-)-strempeliopine was developed. This synthetic strategy featured the palladium-catalyzed decarboxylative asymmetric allylic alkylation of N-benzoy
Palladium-Catalyzed Distal m-C-H Functionalization of Arylacetic Acid Derivatives
Srinivas, Dasari,Satyanarayana, Gedu
, p. 7353 - 7358 (2021/10/01)
Herein, we present m-C-H olefination on derivatives of phenylacetic acids by tethering with a simple nitrile-based template through palladium catalysis. Notably, the versatility of the method is evaluated with a wide range of phenylacetic acid derivatives for obtaining the meta-olefination products in fair to excellent yields with outstanding selectivities under mild conditions. Significantly, the present strategy is successfully exemplified for the synthesis of drugs/natural product analogues (naproxen, ibuprofen, paracetamol, and cholesterol).
CONTINUOUS FLOW SYNTHESIS OF IBUPROFEN
-
, (2021/04/23)
This disclosure generally relates to methods of making ibuprofen, naproxen, and derivatives thereof. This disclosure also generally relates to compounds made by the disclosed methods. This abstract is intended as a scanning tool for purposes of searching in the particular art and is not intended to be limiting of the present invention.