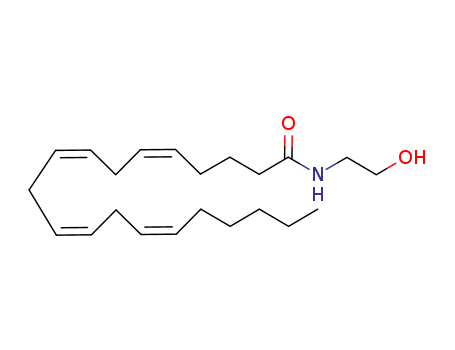
ANANDAMIDE literature
Modification of the antitumor effect of doxorubicin by complexes of α-fetoprotein with amphiphilic compounds based on polyenoic fatty acids
Arsenov,Babitskaya,Vashkevich,Golubeva,Kisel,Kuz'mitskii,Mashkovich,Slabkevich,Strel'chenok
, p. 474 - 477 (2002)
-
Enrichment of arachidonic acid for the enzymatic synthesis of arachidonoyl ethanolamide
Wang, Xingguo,Wang, Xiaosan,Wang, Tong
, p. 1031 - 1039 (2013)
Arachidonoyl ethanolamide is an endogenous cannabinoid neurotransmitter that potentially has therapeutic properties. In this study, we report an enzymatic method to synthesize this bioactive ethanolamide. First, free fatty acids were obtained from arachidonic acid-rich oil and then arachidonic acid was enriched by urea inclusion and AgNO3 solution fractionation. Arachidonic acid content was increased from 40.2 to 78.4 % with 27.6 ± 1.8 % total fatty acid mass yield (w/w, relative to total free fatty acid) after urea inclusion. Purification of arachidonic acid by AgNO3 solution fractionation was optimized, and under the optimal conditions, a product with 90.7 % arachidonic acid was obtained with 80.4 % mass yield (w/w, relative to total free fatty acid). Finally, arachidonoyl ethanolamide was synthesized by reacting the purified arachidonic acid with ethanolamine in hexane using Novozym 435 lipase of Novozymes America (Blair, NE), which resulted in the formation of 88.4 ± 0.6 % arachidonoyl ethanolamide with 72.7 ± 2.2 % mass yield. The main novelties of this study are the enrichment of polyunsaturated fatty acids by AgNO3 solution fractionation which has received little attention in recent years, and this is the first time the synthesis of arachidonoyl ethanolamide is reported.
Methyl arachidonyl fluorophosphonate: A potent irreversible inhibitor of anandamide amidase
Deutsch, Dale G.,Omeir, Romelda,Arreaza, Gladys,Salehani, David,Prestwich, Glenn D.,Huang, Zheng,Howlett, Allyn
, p. 255 - 260 (1997)
Anandamide amidase (EC 3.5.1.4) is responsible for the hydrolysis of arachidonoyl ethanolamide (anandamide). Relatively selective and potent enzyme reversible inhibitors effective in the low micromolar range, such as arachidonyl trifluoromethyl ketone (Arach-CF3), have been described (Koutek et al., J Biol Chem 269: 22937-22940, 1994). In the current study, methyl arachidonyl fluorophosphonate (MAFP), an arachidonyl binding site directed phosphonylation reagent, was tested as an inhibitor of anandamide amidase and as a ligand for the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. MAFP was 800 times more potent than Arach-CF3 and phenylmethylsulfonyl fluoride (PMSF) as an amidase inhibitor in rat brain homogenates. In intact neuroblastoma cells, MAFP was also approximately 1000-fold more potent than Arach-CF3. MAFP demonstrated selectivity towards anandamide amidase for which it was approximately 3000 and 30,000-fold more potent than it was towards chymotrypsin and trypsin, respectively. MAFP displaced [3H]CP-55940 binding to the CB1 cannabinoid receptor with an IC50 of 20 nM vs 40 nM for anandamide. It bound irreversibly and prevented subsequent binding of the cannabinoid radioligand [3H]CP-55940 at that locus. These studies suggest that MAFP is a potent and specific inhibitor of anandamide amidase and, in addition, can interact with the cannabinoid receptors at the cannabinoid binding site. This is the first report of a potent and relatively selective irreversible inhibitor of arachidonoyl ethanolamide amidase.
ANANDAMIDE COMPOUNDS
-
Page/Page column 42-43, (2020/07/25)
The present application provides anandamide and 2-arachidonyl glycerol compounds useful for treating a disease or disorder in a subject in need thereof. Pharmaceutical compositions comprising the compounds and methods of treating diseases or disorders are also provided.
COMPOSITIONS HAVING AN AGENT AND AN ENHANCER THEREOF, METHODS OF USE, AND DELIVERY SYSTEMS
-
, (2020/03/23)
The present invention relates to compositions, and methods of use thereof, related to the endocannabinoid system and includes therapeutic compositions including an agent and an enhancer thereof, optionally, formulated for administration of the therapeutic compositions, preferably in a measured amount.
A Convenient Protocol for the Synthesis of Fatty Acid Amides
Johansson, Silje J. R.,Johannessen, Tonje,Ellefsen, Christiane F.,Ristun, Mali S.,Antonsen, Simen,Hansen, Trond V.,Stenstrom, Yngve,Nolsoe, Jens M. J.
supporting information, p. 213 - 217 (2019/01/14)
Several classes of biologically occurring fatty acid amides have been reported from mammalian and plant sources. Many amides conjugated with fatty acids of mammalian origin exhibit specific activation of individual receptors. Their potential as pharmacological tools or as lead compounds towards the development of novel therapeutics is of great interest. Hence, access to such amides by a practical, high-yielding and scalable protocol without affecting the geometry or position of sensitive functionalities is needed. A protocol that meets all these requirements involves activation of the corresponding acid with carbonyl diimidazole (CDI) followed by reaction with the desired amine or its hydrochloride. More than fifty compounds have been prepared in generally high yields.
INHIBITORS OF N-ACYLPHOSPHATIDYLETHANOLAMINE PHOSPHOLIPASE D (NAPE-PLD)
-
, (2019/12/15)
The invention relates to a compound of the formula (I) as novel inhibitor of N-acylphosphatidylethanolamine phospholipase D (NAPE-PLD), and to use thereof for the prophylaxis or treatment of diseases associated with NAPE-PLD. wherein in a ring A, X1 is N, or CR4; X2 is N or CR5; X3 is N or CH; with the proviso that at least one of X1 and X3 is N.