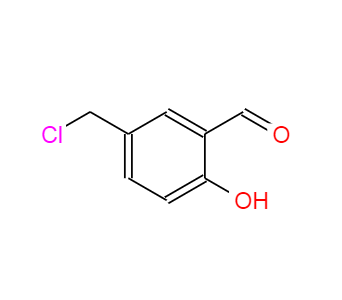
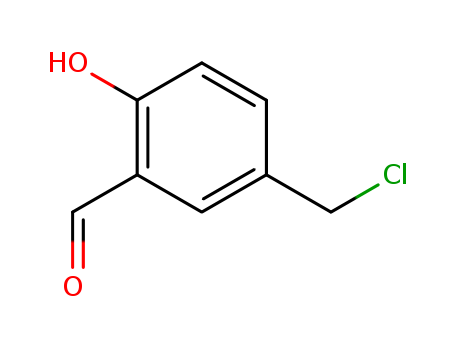
5-(CHLOROMETHYL)-2-HYDROXYBENZALDEHYDE literature
Synthesis of novel bis(chromenes) and bis(chromeno[3,4-C]pyridine) incorporating piperazine moiety
Mekky, Ahmed E. M.,Sanad, Sherif M. H.
, p. 1385 - 1395 (2019)
Novel bis(2-oxo-2H-chromene) as well as bis(2-imino-2H-chromene) derivatives incorporating piperazine moiety were prepared by the cyclocondensation reaction of bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) with two equivalents of each of the appropriate β-ketoesters or acetonitrile derivatives. The bis(2-imino-2H-chromene-3-carbothioamide) derivative was used as a key synthon for construction of novel bis(3-(4-substituted thiazol-2-yl)-2H-chromen-2-one) derivatives via its cyclocondensation with a series of the appropriate α-halocarbonyl derivatives. Moreover, the bis(2-hydroxybenzaldehyde) reacted with four equivalents of the appropriate acetonitrile derivatives to afford the corresponding bis(3H-chromeno[3,4-c]pyridine) derivatives. Elucidation of the structure of the novel bis(chromenes) bearing piperazine nucleus was established by the spectral data and elemental analyses.
Efficient synthesis and evaluation of bis-pyridinium/bis-quinolinium metallosalophens as antibiotic and antitumor candidates
Elshaarawy, Reda F.M.,Eldeen, Ibrahim M.,Hassan, Eman M.
, p. 162 - 173 (2017)
Inspired with the pharmacological diversity of salophens and in our endeavor to explore a new strategy which may conflict the invasion of drug resistance, we report herein efficient synthetic routes for the synthesis of new RO-salophen(Cl), pyridinium/quinolinium-based salophens (3a-e) and metallosalophens (4a-j). These new architectures have been structurally characterized by elemental and spectral analysis as well pharmacologically evaluated for their in?vitro antimicrobial, against a common panel of pathogenic bacterial and fungal strains, and anticancer activities against human colon carcinoma (HCT-116) cell lines. Antimicrobial assay results revealed that all tested compounds exhibited moderate to superb broad-spectrum efficacy in comparison to the standard antibiotic with a preferential ability to perform as a fungicides than to act as bactericides. Noteworthy, VO(II)-salophens are more effective in reduction HCT-116?cell viability than Cu(II)-salophens. For example, VO(II)-salophen3 (4f) (IC50?=?2.13?μg/mL) was ca. 10-fold more efficient than Cu(II)-salophen3 (4e) (IC50?=?20.30?μg/mL).
Computational study on non-linear optical property of Wittig based Schiff-Base ligands (both Z & E isomers) & Copper(II) complex
Rajasekhar, Bathula,Muhammad Hijaz,Swu, Toka
, p. 212 - 222 (2018)
96 new Wittig based Schiff-Base (WSB) ligands (both E & Z conformation) containing fused aromatic rings were designed and screened for NLO property. Wittig based precursor aldehydes were synthesized and spectroscopically confirmed. WSB ligands and their copper(II) complexes were also designed, optimized and their NLO property was studied using a GAUSSIAN09 computer program. For Optimization & Hyperpolarizability (β) calculations, DFT based B3LYP method was applied with LANL2DZ basis set for metal ion and 6-31G* basis set for C, H, N & O atoms. The study presents the Structure-Activity relationship (SAR) between WSB ligands and β. The study revealed that WSB Ligands of the category N2, which are those derived from precursor aldehyde, (2-hydroxy-5-(2-(naphthalen-1-yl)vinyl)benzaldehyde) encoded as PA-2, showed higher β values over N1, which are derived from, 2-hydroxy-5-(2-(naphthalen-1-yl)vinyl)benzaldehyde, encoded as PA-1. Among all ligands, Ligand-14, (E?4-(2-Pyren-1-yl-vinyl)-2-([1,2,4]triazol-4-yliminomethyl)-phenol), of N2 category showed highest β value (6.968 × 10?30 e.s.u). After complexing with Cu(II), encoded as Complex-1 ([(4-(2-Pyren-1-yl-vinyl)-2-([1,2,4]triazol-4-yliminomethyl)-phenoxy)2Cu], which has C2 symmetry, the β value (0.310 × 10?30 e.s.u) unexpectedly decreased. However, it is still high as compared to that of urea (β = 0.091 × 10?30 e.s.u). The output of TD-DFT also supports the obtained results. Different factors affecting β value especially their geometrical isomeric effect were successfully analyzed.
A selective and sensitive near-infrared fluorescent probe for real-time detection of Cu(i)
Liu, Yiqing,Kang, Ting,He, Qian,Hu, Yuefu,Zuo, Zeping,Cao, Zhihua,Ke, Bowen,Zhang, Weiyi,Qi, Qingrong
, p. 14824 - 14828 (2021)
The disruption of copper homeostasis (Cu+/Cu2+) may cause neurodegenerative disorders. Thus, the need for understanding the role of Cu+ in physiological and pathological processes prompted the development of improved methods of Cu+ analysis. Herein, a new near-infrared (NIR) fluorescent turn-on probe (NPCu) for the detection of Cu+ was developed based on a Cu+-mediated benzylic ether bond cleavage mechanism. The probe showed high selectivity and sensitivity toward Cu+, and was successfully applied for bioimaging of Cu+ in living cells. This journal is
A novel ditopic zinc-salophen macrocycle: A potential two-stationed wheel for [2]-pseudorotaxanes
Dalla Cort, Antonella,Mandolini, Luigi,Pasquini, Chiara,Schiaffino, Luca
, p. 4543 - 4546 (2006)
Crown ether macrocycle 1 including a zinc-salophen unit is obtained via a de novo synthetic design to give a potential pH-driven two-stationed wheel component of [2]-pseudorotaxane systems. The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Light-Induced Activation of a Molybdenum Oxotransferase Model within a Ru(II)-Mo(VI) Dyad
Ducrot, Aurélien B.,Coulson, Ben A.,Perutz, Robin N.,Duhme-Klair, Anne-Kathrin
, p. 12583 - 12594 (2016)
Nature uses molybdenum-containing enzymes to catalyze oxygen atom transfer (OAT) from water to organic substrates. In these enzymes, the two electrons that are released during the reaction are rapidly removed, one at a time, by spatially separated electron transfer units. Inspired by this design, a Ru(II)-Mo(VI) dyad was synthesized and characterized, with the aim of accelerating the rate-determining step in the cis-dioxo molybdenum-catalyzed OAT cycle, the transfer of an oxo ligand to triphenyl phosphine, via a photo-oxidation process. The dyad consists of a photoactive bis(bipyridyl)-phenanthroline ruthenium moiety that is covalently linked to a bioinspired cis-dioxo molybdenum thiosemicarbazone complex. The quantum yield and luminescence lifetimes of the dyad [Ru(bpy)2(L2)MoO2(solv)]2+ were determined. The major component of the luminescence decay in MeCN solution (?., = 1149 ± 2 ns, 67%) corresponds closely to the lifetime of excited [Ru(bpy)2(phen-NH2)]2+, while the minor component (?., = 320 ± 1 ns, 31%) matches that of [Ru(bpy)2(H2-L2)]2+. In addition, the (spectro)electrochemical properties of the system were investigated. Catalytic tests showed that the dyad-catalyzed OAT from dimethyl sulfoxide to triphenyl phosphine proceeds significantly faster upon irradiation with visible light than in the dark. Methylviologen acts as a mediator in the photoredox cycle, but it is regenerated and hence only required in stoichiometric amounts with respect to the catalyst rather than sacrificial amounts. It is proposed that oxidative quenching of the photoexcited Ru unit, followed by intramolecular electron transfer, leads to the production of a reactive one-electron oxidized catalyst, which is not accessible by electrochemical methods. A significant, but less pronounced, rate enhancement was observed when an analogous bimolecular system was tested, indicating that intramolecular electron transfer between the photosensitizer and the catalytic center is more efficient than intermolecular electron transfer between the separate components.
Experimental evaluation of cationic-Schiff base surfactants based on 5-chloromethyl salicylaldehyde for improving crude oil recovery and bactericide
Al-Sabagh, Ahmed M.,Betiha, Mohamed A.,El-Henawy, Samy B.,Mahmoud, Tahany,Negm, Nabel A.
, (2020)
In this study, a new family of cationic and cationic–Schiff Base surfactant was synthesized namely; N-(3-formyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)-N, N-dimethylhexadecan-1-aminium chloride (FHDHAC), (E)-N-(3-((butylimino)methyl)-4-hydroxybenzyl)-N,N-dimethylhexadecan-1-aminium chloride (4-IMHDAC), (E)-N-(3-((hexylimino)methyl)-4-hydroxybenzyl)-N,N-dimethylhexadecan-1-aminium chloride (6-IMHDAC) and (E)-N-(4-hydroxy-3-((octylimino) methyl)benzyl)-N,N-dimethylhexadecan-1-aminium chloride (8-IMHDAC) were prepared from 5-chloromethyl salicylaldehyde compound (5-CMS). The chemical structures of 5-CMS, 4-IMHDAC, 6-IMHDAC, and 8-IMHDAC are characterized using FTIR, 1H NMR instruments. The surface activity measurements of the prepared compounds showed a gradual increase in surface activity by increasing the alkyl chain length. Adsorption and micellization thermodynamic functions revealed the higher tendencies of the different surfactants towards adsorption at the organic/polar phase. The synthesized surfactants were evaluated in the enhanced oil recovery process and showed excellent efficiency (63.98%, 71.25%, and 75.72% for 4-IMHDAC, 6-IMHDAC, and 8-IMHDAC, respectively) during the recovery process near their critical micelle concentrations. The prepared surfactants showed high antimicrobial efficacy against different bacteria and fungi.
Synthesis and Antimicrobial Activity of (3-Formyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium Chloride Acylhydrazones
?ivkovi?-Radovanovi?, V.,Andjelkovi?, L.,Milenkovi?, M. R.
, p. 1716 - 1720 (2020)
Abstract: In this study, four novel quaternary phosphonium acylhydrazones, derivatives of (3-formyl-4-hydroxybenzyl)triphenylphosphonium chloride, have been synthesized and their structures elucidated from IR and NMR spectra, and elemental analysis. All synthesized compounds have been tested for their antimicrobial activity, and acylhydrazones have demonstrated selective activity against Gram-positive bacteria strains.
Topoisomerase i inhibition and DNA cleavage by zinc, copper, and nickel derivatives of 2-[2-bromoethyliminomethyl]-4-[ethoxymethyl]phenol complexes exhibiting anti-proliferation and anti-metastasis activity
Lee, Sze Koon,Tan, Kong Wai,Ng, Seik Weng
, p. 14 - 21 (2016)
Three transition metal derivatives (Zn, Cu, and Ni) of 2-[2-bromoethyliminomethyl]-4-[ethoxymethyl]phenol (L) were synthesized by the reaction of the metal salts with the Schiff base ligand in one pot. In the crystal structure of [Zn(L)Br], the Schiff base ligand binds to the metal center through its phenolate oxygen and imine nitrogen, and adopts a distorted tetrahedral geometry. These compounds were found to inhibit topoisomerase I (topo I) activity, induce DNA cleavage and show DNA binding activity. Moreover, these compounds were found to be cytotoxic towards several cancer cell lines (A2780, MCF-7, HT29, HepG2, A549, PC3, LNCaP) and prevent metastasis of PC3. Collectively, Cu(II) complex 2 shows superior activity relative to its Zn(II) and Ni(II) analogs.
Preparation of monodispersed metal-based infinite coordination polymer nanostructures and their good capability for metal oxide preparation
Mohammadikish, Maryam,Ghanbari, Sara
, p. 86 - 90 (2018)
Two coordination polymer particles (Zn-CPP and Pb-CPP) were synthesized by reaction of metal(II) acetates with the sodium {3-[(4-carboxy-phenylimino)-methyl]-4-hydroxy-benzylsulfanyl}-acetate. The composition of CPPs was determined by elemental analyses which confirmed the presence of two metal ions per one organic linker in each monomeric unit. Photoluminescence studies of the prepared CPPs showed good correlation between the structure of CPPs and emission wavelengths. The calcination of Zn-CPP produced zinc oxide nanoparticles with large band gap and well defined morphology and composition.
Polymer complexes XXXVII novel models and structural of symmetrical poly-Schiff base on heterobinuclear complexes of dioxouranium(VI)
El-Sonbati,El-Bindary,Rashed
, p. 1411 - 1424 (2002)
Some binary and ternary novel complexes of dioxouranium(VI) with 5-vinylsalicylaldehyde (VSH) have been prepared and characterized by various physico-chemical techniques. The amine exchange reactions of coordinated poly-Schiff bases in these complexes have been also carried out which give symmetrical tetradentate poly-Schiff base complexes. Metal exchange reaction of these dioxouranium(VI) complexes with copper(II) gives the corresponding Cu(II) complexes. Reaction of tetradentate poly-Schiff base complexes of Cu(II) so obtained with ZrCl4 gives heterobinuclear polymer complexes. Magnetic, electronic and IR spectral information commensurate that configurations of square planar copper(II) polymer complexes. All the polymer complexes are coloured and appear to be nonelectrolytes in DMF. The ligands behave as bi-(O, O) and tetradentate (N2, O2) donors. El-Sonbati equation was used to evaluate the symmetric stretching frequency from which the fU-O and fUO, UO- were calculated.
Oxovanadium(iv) and iron(iii) salen complexes immobilized on amino-functionalized graphene oxide for the aerobic epoxidation of styrene
Li, Zhifang,Wu, Shujie,Ding, Hong,Lu, Haiming,Liu, Jiayin,Huo, Qisheng,Guan, Jingqi,Kan, Qiubin
, p. 4220 - 4229 (2013)
Oxovanadium(iv) and iron(iii) salen complexes grafted onto amino-modified graphene oxide (NH2-GO) have been synthesized via a stepwise procedure and the prepared materials were used as heterogeneous catalysts in the aerobic oxidation of styrene. The structures of these materials have been thoroughly investigated using different characterization techniques such as XRD, N2 adsorption-desorption, TEM, FT-IR, diffuse reflectance UV-visible spectroscopy, ICP-AES, TEM, TG, Raman, and XPS. The results of XRD, N 2 adsorption-desorption and TEM revealed that the structures of the prepared catalysts were well preserved. In addition, the results of FT-IR, diffuse reflectance UV-visible spectroscopy, ICP-AES, TG, Raman and XPS suggested that the oxovanadium(iv) and iron(iii) complexes had been incorporated onto amino-modified graphene oxide (GO). It was found that the heterogeneous oxovanadium(iv) catalyst was more active than its homogeneous analogue in the epoxidation of styrene, using acetonitrile as solvent and air as the oxidant in combination with the sacrificial co-reductant isobutyraldehyde, due to site-isolation. Furthermore, the tethered vanadium catalyst was quite stable and could be recycled many times.
Structural and cytotoxic studies of cationic thiosemicarbazones
Sinniah, Saravana Kumar,Sim, Kae Shin,Ng, Seik Weng,Tan, Kong Wai
, p. 253 - 259 (2017)
Schiff bases from the thiosemicarbazones family with variable N4 substituents are known to show enhanced growth inhibitory properties. In view of these facts and as a part of our continuous interest in cationic Schiff bases, we have developed several Schiff base ligands from (3-formyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)methyltriphenylphosphonium (T) in present study. The compounds were characterized by various spectroscopic methods (infrared spectra, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, HRESIMS and X-ray crystallography). Three of the N4 substituents, namely P(tsc)T, FP(tsc)T and EP(tsc)T exerted strong growth inhibitory properties by inhibiting the highly metastasis prostate cancer growth (PC-3). The thiosemicarbazone with ethylphenyl (EP) moiety displayed most potent activity against all cell lines tested. The MTT data obtained from analysis establishes that phenyl substituent enhances the growth inhibitory properties of the compound. The result affirms that EP(tsc)T would serve as a lead scaffold for rational anticancer agent development.
Microwave-Assisted Synthesis of Novel Bis(thiazoles) Incorporating Piperazine Moiety
Mekky, Ahmed E. M.,Sanad, Sherif M. H.
, p. 1560 - 1566 (2019)
Novel bis(hydrazinecarbothioamide) was prepared by the reaction of 1,4-bis[(3-formyl-4-hydroxyphenyl)methyl]piperazine with thiosemicarbazide. The bis(hydrazinecarbothioamide) was used as a building block for construction of a novel bis(thiazolyl)piperazines via its cyclocondensation with a series of each of α-halocarbonyl compounds and hydrazonoyl halides in dimethylformamide in the presence of triethylamine as a catalyst under microwave irradiation. The structure of the newly bis(thiazolyl)piperazine derivatives is elucidated via the spectral data as well as elemental analyses.
Synthesis, characterization and catalytic properties of heterogeneous iron(III) tetradentate Schiff base complexes for the aerobic epoxidation of styrene
Yang, Ying,Guan, Jingqi,Qiu, Pengpeng,Kan, Qiubin
, p. 263 - 270 (2010)
A series of hybrid mesoporous SBA-15 materials containing four iron(III) Schiff base complexes of the type [FeLx(NO3)] (x = 4-7, L = N,N′-bis(salicylidene) ethylenediamine, N,N′-bis(salicylidene) diethylenetriamine, N,N′-bis(salicylidene)o-phenylenediamine, N,N′-bis(3-nitro-salicylidene)ethylenediamine) was synthesized by a post-grafting route. The XRD, N2 adsorption/desorption and TEM measurements confirmed the structural integrity of the mes-oporous hosts, and the spectroscopic characterization tech-niques(FT-IR, UV-visspectroscopy, 1HNMR)confirmedthe ligands and the successful anchoring of iron(III) Schiff base complexes over the modified mesoporous support. Quantification of the supported ligand and metal was carried out by TG/DSC and ICP-AES techniques. The catalyst FeL7-SBA resulting from N,N′-bis(3-nitro- salicylidene)ethylenediamine) ligand was considerably active for the aerobic epoxidation of styrene, in which the highest conversion of styrene reached 83.6%, and the selectivity to styrene oxide was 83.0%. Moreover, it was also found that the catalytic activity increases with the decrease inthe electron-donating ability of the Schiff bases, and the selectivity varies according to the types of substituents in the ligands. Springer Science+Business Media B.V. 2009.
Improving heavy oil recovery, part (I): Synthesis and surface activity evaluation of some novel organometallic surfactants based on salen-M complexes
Abdelhamid,Rizk,Betiha,Desouky,Alsabagh
, p. 1750 - 1761 (2021)
This study focuses on preparing a new family of organometallic surfactants based on five ion complexes, namely Co2+, Ni2+, Cu2+, Fe3+, and Mn2+. The first step is the preparation of 5-chloromethyl salicylaldehyde (Salen, S). The second step is the formation of sodium alkoxide of Pluronic F-127 (AP). The third step is the formation of the modified AP-Salen (new ligand). This ligand was reacted with the metal chlorides as mentioned earlier to obtain the organometallic surfactants (OMS) named AP-Salen-M complexes. FT-IR, 1H-NMR, SEM, and EDX justified the chemical structure of the as-prepared materials. The surface tension of these surfactants was measured for surfactant solutions at different concentrations to determine the CMC and calculate their surface-active properties. The interfacial tension at CMC was measured against heavy crude oil to predict the availability and use these surfactants in the enhanced oil recovery (EOR) process. From the results, this class of surfactants exhibited good surface-active properties and high efficiency on the interface adsorption; besides, they reduced the interfacial tension in the order between 10-1 and 10-2 mN m-1, which gives a good indication to use these surfactants in EOR application for the heavy crude oil.
DNA/BSA binding of a new oxovanadium (IV) complex of glycylglycine derivative Schiff base ligand
Asadi, Zahra,Kalantari, Razieh
, (2020)
In this study, a new oxovanadium (IV) Schiff base complex was synthesized by the reaction of {[5-(triethylammoniummethyl)salicylaldehyde]chloride}triethylammonium and vanadyl sulfate. The complex was characterized by elemental analysis, FT-IR and UV–Vis spectroscopy. The interaction between the complex and bovine serum albumin (BSA) was studied by absorption and emission titration methods. The quality of the spectral changes and the large calculated value of both the binding constant (Kb = 7.53 × 104 M?1) and the Stern-Volmer quenching constant (KSV = 7.65 × 104 M?1) proved the strong affinity of the complex to BSA. The static quenching mechanism was confirmed by comparing the calculated Kb values at four different temperatures. The negative changes in enthalpy and Gibbs free energy, proved that the BSA-complex binding is exothermic and spontaneous. The fluorescence data also indicated 1:1 binding stoichiometry of the complex on one binding site of BSA. Competitive experiments with site markers (phenylbutazone and ibuprofen) and synchronous measurements identified site I of BSA as the main binding site. Molecular docking results confirmed the binding pocket of site I (subdomain IIA) as the binding site. In the second part of the work, the binding of the complex to fish sperm DNA (FS-DNA) was investigated by UV–Vis absorption spectroscopy, fluorescence spectroscopy, viscosity measurement and cyclic voltammetry. The Stern-Volmer quenching and bimolecular quenching rate constants (KSV = 6.13 × 102 M?1, kq = 6.13 × 1010 M?1S?1) were calculated. Absorption and emission studies could present types of interactions for example groove binding and electrostatic. A minor changes in viscosity showed a groove binding mode. In cyclic voltammogram study, decrease in current and also shift of peak potentials positively after adding DNA supported a partial intercalation mode. Theoretical docking study proposed the minor groove as the main part for DNA-complex binding.
Covalently functionalized carbon nanoparticles with a chiral Mn-Salen: A new nanocatalyst for enantioselective epoxidation of alkenes
Zammataro, Agatino,Gangemi, Chiara Maria Antonietta,Pappalardo, Andrea,Toscano, Rosa Maria,Puglisi, Roberta,Nicotra, Giuseppe,Fragalà, Maria Elena,Tuccitto, Nunzio,Sfrazzetto, Giuseppe Trusso
, p. 5255 - 5258 (2019)
A new protocol to obtain carbon nanoparticles (CNPs) covalently functionalized with a chiral Mn-Salen catalyst is described here. The new nanocatalyst (CNPs-Mn-Salen) was tested in the enantioselective epoxidation of some representative alkenes (CN-chromene, 1,2-dihydronaphthalene and cis-β-ethyl styrene), obtaining better enantiomeric excess values than that of the catalyst single molecule, highlighting the role of the nanostructure in the enantioselectivity.
A new fluorescence chemosensor based on benzothiazole derivative for Zn2+ and its logic gate behavior
Hu, Jing-Han,Qi, Jing,Sun, You,Pei, Peng-Xiang
, p. 565 - 569 (2017)
A novel benzothiazole derivative J as a fluorescent chemosensor for Zn2+ has been designed and synthesized. The chemosensor J exhibits high selectivity and sensitivity to Zn2+ as fluorescence “turn-on” behavior, which the other cations do not make sense. The detection limit calculated by fluorescence titration method was 1.64 × 10?8 M. Furthermore, the generated J-Zn2+ ensemble could recover the enhanced fluorescence upon the addition of EDTA generating an “on-off-on” recycle. In addition, the test strip based on J was fabricated, which could act as a convenient and efficient Zn2+ test kit.
Simple preparation of amorphous infinite coordination polymer nanoparticles and solid state transformation to ZnO nanoparticles
Mohammadikish, Maryam,Molla, Fatemeh
, p. 340 - 346 (2019)
A novel organic-inorganic hybrid materials comprised from infinite-chains of Zn(II) and bi-carboxylic acid linker (4-Carboxy-1-{3-[(4-carboxy-phenylimino)-methyl]-4-hydroxy-benzyl}-pyridinium chloride) was successfully formed by precipitation from the mixture of precursor solutions. Thermogravimetric and elemental analyses, energy dispersive X-ray (EDX) and Fourier-transform infrared (FT-IR) spectroscopies approved the existence of two well-defined coordinating sites (N,O and COO sites) coordinated to zinc ions. Coordination of the linker N,O site to Zn2+ ion generated the metalo-ligand units and further addition of Zn2+ ion resulted in the attachment of these units to each other via carboxylic acid groups. Time-dependent SEM analysis demonstrated that the optimum time for preparing the smallest particles is 5 min. Calcination of the prepared zinc based coordination polymer achieved uniform ZnO nanoparticles with larger band gap in comparison with bulk counterpart.
Nerve Gas Simulant Sensing by a Uranyl–Salen Monolayer Covalently Anchored on Quartz Substrates
Trusso Sfrazzetto, Giuseppe,Millesi, Salvatrice,Pappalardo, Andrea,Tomaselli, Gaetano A.,Ballistreri, Francesco P.,Toscano, Rosa Maria,Fragalà, Ignazio,Gulino, Antonino
, p. 1576 - 1583 (2017)
A uranyl complex monolayer that easily allows the optical detection of a nerve gas simulant, namely, dimethyl methylphosphonate, is reported. Both UV/Vis spectroscopy and photoelectron data confirm that the functional hybrid material coordinates a Lewis base by means of the P=O group, which interacts with the uranium equatorial site available for complexation.
Synthesis of polymer-supported Br?nsted acid-functionalized Zn–porphyrin complex, knotted with benzimidazolium moiety for photodegradation of azo dyes under visible-light irradiation
Khajone, Vijay B.,Bhagat, Pundlik R.
, p. 783 - 802 (2020)
Abstract: A polymer-supported Br?nsted acid-functionalized Zn–porphyrin complex, knotted with benzimidazolium moiety (PSBAZnPP), has been synthesized and characterized by Fourier transform nuclear magnetic resonance (FT-NMR) and Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy (FTIR). The thermal stability was determined by thermogravimetric analysis (TGA), and surface morphology and elemental composition were investigated by scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive spectroscopy (SEM/EDAX). The heterogeneous PSBAZnPP showed high efficacy as a photocatalyst for degradation of azo dyes, such as methyl red (MR), methyl orange (MO) and Congo red (CR), in the presence of visible-light irradiation at ambient condition using atmospheric air/H2O2. The concentration of the dyes was measured by UV–visible spectroscopy, and the degradation of the dyes was confirmed by GC–MS analysis. Further decolorization and degradation of MO were confirmed by using ultra-high-pressure liquid chromatography (UPLC). The optimum degradation was achieved by adding 10?mg catalyst for all azo dyes for 60?min in the presence of air. The effect of scavengers was studied to indicate the most active species generated during photocatalysis. PSBAZnPP furnished a good response toward the photodegradation of MR, MO and CR under optimized conditions. Finally, the mechanism of photocatalytic degradation process was suggested. Relevant active species produced in the PSBAZnPP/H2O2 or PSBAZnPP/air system under visible light were recognized by using different types of scavengers, viz. EDTA, p-benzoquinone (PBQ), terephthalic acid (TPA), sodium azide and sodium nitrate, for determination of formation of holes, O2·, OH ·, 1O 2 and an aqueous electron (e?), respectively. The comparative acidity of the synthesized PSBAZnPP catalyst was measured using UV–Vis and then equated to relations of the Hammett value (H0). The efficiency of catalyst correlates with a considerable proton level required for degradation of organic dyes. Graphic abstract: [Figure not available: see fulltext.]
Turn-on pH nano-fluorosensor based on imidazolium salicylaldehyde ionic liquid-labeled silica nanoparticles
Ali, Reham,Saleh, Sayed M.,Elshaarawy, Reda F. M.
, p. 86965 - 86975 (2016)
A new simple pH-sensitive fluorescent probe, methylimidazolium salicylaldehyde ionic liquid (MeIm-Sal-IL), was designed and successfully synthesized from commercially available salicylaldehyde (Sal) via an extremely simple efficient two-step synthetic protocol. This new pH sensor has prominent advantages over traditional fluorescent pH probes, such as a large Stokes shift (~125 nm) and extreme aqueous solubility along with simultaneous color and fluorescence profile changes as a result of pH alteration. The fluorescence behavior of this new probe provides a new state-of-the-art pH sensing method. Fluorescence turn-on is observed with increasing pH (≈5 to 11), accompanied by a bathochromic shift of 70 nm from (λmax emission 435 to 505 nm; λmax absorption 323 to 378 nm). This bathochromic shift may be ascribed to the tautomeric equilibrium involving excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT). Meanwhile, the fluorescence intensity enhancement at higher pH is attributable to the internal charge transfer (ICT) process. Also, the new probe was labeled with silica nanoparticles (SiNPs) in order to produce a novel nano-fluorosensor for pH measurements. The nanosensor was fabricated by covalent labeling of chloro-modified SiNPs with the new probe. The emission spectra of the new nanosensors are bathochromically shifted by about 65 nm (λmax emission 435 to 500 nm) at low pH (3 to 5). Moreover, the fluorescence intensity of the nanosensor is increased by ≈60 fold in the pH range from 5 to 9. The sensitivity of the new nanosensor is highly applicable within the pH range of 5 to 9, which suggests a broad variety of applications in the physiological pH range.
Novel metal complexes for D-(A-π-A)2 motif dye sensitizer: Synthesis and photovoltaic application
Zhang, Houpeng,Wu, Xianming,Tang, Shiyu,Wang, Kaixuan,Tian, Yong,Zhong, Chaofan
, (2021)
Four metal complexes BDTT-PCd, BDTT-PZn, BDTT-PCu, and BDTT-PCo with the symmetrical structure were designed, synthesized, and characterized, which would be used as D-(A-π-A)2 motif dye sensitizers. These complexes adopt Cd(II), Zn(II), Cu(II), and Co(II) complexes as auxiliary electron acceptors (A), thienylbenzo[1,2-b:4,5-b′]dithiophene (BDTT) as electron donor (D), and the 8-quinolinol derivative as the π bridge and the acceptor (A) of D-(A-π-A)2 motif dye sensitizers. The photophysical, electrochemical, and photovoltaic properties of these complexes have been investigated. The four complexes-based dye-sensitized solar cells (DSSCs) device exhibited a short-circuit photocurrent density (Jsc) of 17.51, 17.02, 15.07, and 14.38 mA cm?2 and an attractive power conversion efficiency (η) of 8.82%, 8.32%, 8.03%, and 7.55%, respectively, under the AM 1.5 irradiation (100 mW cm?2). The photovoltaic conversion efficiency (PCE) and the short-circuit photocurrent density (Jsc) of BDTT-PCd, BDTT-PZn, BDTT-PCu, and BDTT-PCo are sequentially reduced; it attributed to the difference of the electron-withdrawing ability of the auxiliary acceptor resulted by the difference of coordination abilities of metal ions Cd(II), Zn(II), Cu(II), and Co(II) with ligand. These results provide strong evidence that D-(A-π-A)2 motif complexes has great potential as promising photosensitizers in the applications of DSSCs.
A selective quinoline-derived fluorescent chemodosimeter to detect cyanide in aqueous medium
Razi, Syed S.,Ali, Rashid,Srivastava, Priyanka,Misra, Arvind
, p. 1052 - 1056 (2014)
A simple quinoline derived probe 3 has been described. Probe 3 having aldehyde function upon interaction with cyanide undergo nucleophilic addition reaction to form cyanohydrin derivative 4 in which fluorescence intensity enhances significantly, 'turn-on' by photoinduced electron transfer (PET) OFF-ON mechanism. The color of probe solution switched-on to fluorescent blue which is visible to the naked-eye. Job's plot analysis revealed a 1:1 stoichiometry for an interaction between 3 and cyanide along with detection limit 0.058 μM (1.5 ppb). The mode of interaction to detect cyanide in aqueous medium through a reaction based chemodosimeter approach has been confirmed by NMR, mass, FTIR, and DFT data analysis.
Structural Identification of Products from the Chloromethylation of Salicylaldehyde
Kadwa, Ebrahim,Friedrich, Holger B.,Bala, Muhammad D.
, p. 44 - 48 (2019)
In the functionalization of salicylaldehyde to give 5-(chloromethyl)salicylaldehyde, two byproducts [5-(hydroxymethyl)salicylaldehyde and 5,5′-methylenebis(salicylaldehyde)] were also isolated. Detailed characterizations and structural analyses of all three products by single-crystal X-ray diffraction, multinuclear NMR spectroscopy, high-resolution mass spectrometry, and IR spectroscopic techniques are presented and discussed. A strategy is presented for the preferential isolation of the two byproducts through column chromatography.
Facile synthesis of novel zinc-based infinite coordination polymer nanoparticles
Mohammadikish,Ahmadvand-Akradi
, p. 48 - 51 (2017)
-
Synthesis, in-vitro and in-silico study of novel thiazoles as potent antibacterial agents and MurB inhibitors
Ahmed, Ahmed A. M.,Mekky, Ahmed E. M.,Sanad, Sherif M. H.
, (2020)
Efficient procedures are herein reported for the synthesis of novel hybrid thiazoles via a one-pot three-component protocol. The protocol involves the reaction of novel aldehyde, thiosemicarbazide and halogen-containing reagents in solvent- and catalyst-free conditions. The structures of the new thiazoles were elucidated by elemental analyses and spectroscopic data. The in-vitro antibacterial screening and MurB enzyme inhibition assays were performed for the novel thiazoles. The thiazol-4(5H)-one derivative 6d, with p-MeO, exhibits the best antibacterial activities with minimum inhibitory concentration values of 3.9, 3.9, 7.8, and 15.6 μg/ml against Staphylococcus aureus, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Streptococcus mutans, and Escherichia coli, respectively, as compared to the reference antibiotic drugs. It also exhibits the highest inhibition of the MurB enzyme with an IC50 of 8.1 μM. The structure–activity relationship was studied to determine the effect of the structures of the newly prepared molecules on the strength of the antibacterial activities. Molecular docking was also performed to predict the binding modes of the new thiazoles in the active sites of the E. coli MurB enzyme.
Substitution of PPh3+ as a lipophilic cation on new water-soluble Co(II) and Zn(II) Schiff base complexes: Effect of central metal and substitutional group of ligand on DNA-complex interaction
Asadi, Zahra,Haddadi, Elahe,Sedaghat, Moslem
, p. 140 - 150 (2017)
New series of water soluble Schiff base complexes by conjugating the lipophilic triphenylphosphonium cation to aromatic moiety of Schiff base ligand, aiming to increase the water solubility and passing through cell membrane were synthesized and characterized. Four new complexes; [N,N′-bis{5-[(triphenylphosphoniumchloride)-methyl]salicylidine}-phenylenediamine] with the formula [Zn(5-CH2PPh3-4-H-1,2-salphen)] (ClO4)2 (1), [Zn(5-CH2PPh3-4-CH3-1,2-salphen)](ClO4)2 (2), [Zn(5-CH2PPh3-4-Cl-1,2-salphen)](ClO4)2 (3), [Co(5-CH2PPh3-4-CH3-1,2-salphen)](ClO4)2 (4) were characterized by elemental analysis, FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, 31P NMR and UV–vis spectroscopy. Cobalt(II) complex also characterized by thermal gravimetry analysis (TG). DNA interaction studies were investigated by UV–vis absorption spectroscopy, viscosity measurements, circular dichroism (CD) spectroscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy. The DNA binding affinity (Kb) obtained from absorption spectroscopy had this order: 2?>?3?>?4?>?1?>?ligand(L) which revealed that metal complexes had more propensities to interact with DNA. In comparing the metal complexes; Zn(II) complexes revealed DNA binding stronger than the corresponding Co(II) analogue. All the complexes displayed cytotoxicity against Raji, Jurkat and A549 cell lines with potency more than that of cisplatin and thus they are good candidate to act as promising anticancer drug. Finally, docking studies were performed to further investigate the DNA binding interactions.
A simple pincer-type chemosensor for reversible fluorescence turn-on detection of zinc ion at physiological pH range
Lin, Qi,Cai, Yi,Li, Qiao,Chang, Jing,Yao, Hong,Zhang, You-Ming,Wei, Tai-Bao
, p. 4162 - 4167 (2015)
A new, highly selective and sensitive pincer-type chemosensor (Y) for zinc ion with turn-on fluorescence behavior in physiological pH range solution was developed. Y is based on bi-hydrazone derivatives, which contain pyridine as the fluorescent group and a hydrazone bond as recognition site. The selectivity mechanism of Y for zinc is based on the combined effects of the inhibition of excited-state intramolecular proton transfer (ESIPT) and -HC=N- isomerization, as well as chelation-enhanced fluorescence. The entire process takes less than 15 seconds. The minimum detection limit of Y for zinc reaches 1.39 × 10-8 M. Moreover, Y can conveniently detect zinc in test strip form, and it can be recycled.
Enhanced aerobic epoxidation of styrene with copper(II), cobalt(II), iron(III), or oxovanadium(IV) salen complexes immobilized onto carbon-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles hybridized with graphene sheets
Li, Zhifang,Wu, Shujie,Zheng, Dafang,Ding, Hong,Wang, Xiufang,Yang, Xiaoyuan,Huo, Qisheng,Guan, Jingqi,Kan, Qiubin
, p. 716 - 724 (2014)
Core-shell structural magnetic nanocatalysts, involving carbon-coated magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide sheets (mildly reduced graphene oxide (MRGO)/Fe3O4@C) and carbonaceous coatings on magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles (Fe3O4@C), for immobilizing metal (CuII, CoII, FeIII or VOIV)-salen complexes were prepared by a facile, green, and efficient chemical approach and first applied in the aerobic epoxidation of styrene with air as the oxidizing agent. The prepared catalysts were characterized by different techniques, such as XRD, TEM, FTIR spectroscopy, inductively coupled plasma atomic emission spectroscopy, TEM, thermogravimetric analysis, Raman spectroscopy, and X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy. The magnetic nanocatalysts MRGO/Fe3O 4@C-salen-M (M=Cu, Co, Fe, or V) exhibited higher catalytic reactivity than that of the corresponding Fe3O4@C-salen-M (M=Cu, Co, Fe, or V) species possibly owing to site isolation, good dispersion of magnetic Fe3O4 nanoparticles, and an efficiently synergistic effect between the metal complexes and the supports. Furthermore, MRGO/Fe3O4@C-salen-Co exhibited up to 92.3% conversion of styrene and 59.2% selectivity to the styrene oxide upon using air as the oxidizing agent and showed good recoverability with negligible loss in activity and selectivity within successive runs owing to superparamagnetism. Most importantly, these materials can be easily recovered by simple magnetic separation. Extra support: Core-shell-structured magnetic nanocatalysts have been prepared and used as efficient heterogeneous catalysts for the aerobic oxidation of styrene. Mildly reduced graphene oxide (MRGO; see picture)/Fe 3O4@C-salen-Co showed over 91% conversion of styrene and over 52% selectivity to the styrene oxide. The materials can be easily recovered through simple magnetic separation. Copyright
A functional applied material on recognition of metal ion zinc based on the double azine compound
Wei, Taibao,Liang, Guoyan,Chen, Xiaopeng,Qi, Jin,Lin, Qi,Zhang, Youming,Yao, Hong
, p. 2938 - 2942 (2017)
A colorimetric and fluorescent probe L has been designed and synthesized, which bearing the double azine moiety and showing a detection limit of 2.725?×?10?7?M towards Zn2+. Based on the basic recognition mechanism of ESIPT and CHEF effect, the L has high selectivity and sensitivity to only Zn2+ (not Fe3+, Hg2+, Ag+, Ca2+, Co2+, Ni2+, Cd2+, Pb2+, Cr3+, and Mg2+) within the physiological pH range (pH?=?7.0–8.4) and showed a fluorescence switch. Moreover, this detection progress occured in the DMSO/H2O?~?HEPES buffer (80/20, v/v; pH 7.23) solution which can conveniently used on test strip.
Synthesis, characterization, DNA binding, cleavage activity, cytotoxicity and molecular docking of new nano water-soluble [M(5-CH2PPh3-3,4-salpyr)](ClO4)2 (M = Ni, Zn) complexes
Mandegani, Zeinab,Asadi, Zahra,Asadi, Mozaffar,Karbalaei-Heidari, Hamid Reza,Rastegari, Banafsheh
, p. 6592 - 6611 (2016)
Some new water soluble complexes [N,N′-bis{5-[(triphenyl phosphonium chloride)-methyl]salicylidine}-3,4-diaminopyridine] M(ii), which are formulated as nano-[Zn(5-CH2PPh3-3,4-salpyr)](ClO4)2 (1), [Zn(5-CH2PPh3-3,4-salpyr)](ClO4)2 (2), nano-[Ni(5-CH2PPh3-3,4-salpyr)](ClO4)2 (3), [Ni(5-CH2PPh3-3,4-salpyr)](ClO4)2 (4), and [N,N′-bis{5-[(triphenyl phosphonium chloride)-methyl]salicylidine}-2,3-diaminopyridine]Ni(ii) [Ni(5-CH2PPh3-2,3-salpyr)](ClO4)2 (5) have been isolated and characterized by elemental analysis, FT-IR, 1H NMR, 13C NMR, 31P NMR, and UV-vis spectroscopy. The morphology and size of the nano complexes were determined using FE-SEM and TEM. In vitro DNA binding studies were investigated by UV-vis absorption spectroscopy, viscosity measurements, CD spectroscopy, cyclic voltammetry, emission spectra and gel electrophoresis, which suggest that the metal complexes act as efficient DNA binders. The absorption spectroscopy of the compounds with DNA reveals that the DNA binding affinity (Kb) has this order: 3 > 4 > 5 > 1 > 2 > Ligand. The metal complexes show DNA binding stronger than the ligand, which is expected due to the nature of the metal. The nano complexes display DNA binding stronger than the other complexes which is related to the effect of size on binding affinity and the Ni(ii) complexes reveal DNA binding stronger than the corresponding Zn(ii) analogues, which is expected due to their z? effect and geometry. The prominent double strand DNA cleavage abilities of compound 3 are observed in the absence of H2O2 with efficiencies of more than 50% even at 70 μM complex concentration. Surprisingly, Zn(ii) complexes (compounds 1 & 2) exhibit a higher cytotoxicity (IC50: 7.3 & 10.9 μM at 24 h; IC50: 4.6 & 8.7 μM at 48 h) against human hepatoma (HepG2) and HeLa cell lines than the Ni(ii) complexes (compounds 3, 4 & 5) and 5-fluorouracil as control in spite of their inability to cleave DNA. Finally, DNA binding interactions were performed by docking studies. Density functional theory (DFT) studies were performed using the GAUSSIAN 03 program. The DFT method with B3LYP functional, LANL2DZ basis set for metal centers and 6-311g? for other atoms was used. The synthesized compounds and DNA were simulated by molecular docking to explore more details of the ligands conformation and their orientations in the active site of the receptor.
Dioxomolybdenum(VI) complex covalently attached to amino-modified graphene oxide: Heterogeneous catalyst for the epoxidation of alkenes
Li, Zhifang,Wu, Shujie,Zheng, Dafang,Liu, Jiayin,Liu, Heng,Lu, Haiming,Huo, Qisheng,Guan, Jingqi,Kan, Qiubin
, p. 317 - 323 (2014)
Transition metal salen complex MoO2-salen was successfully tethered onto amino-functionalized graphene oxide (designated as MoO 2-salen-GO), which was tested in the epoxidation of various alkenes using tert-butylhydroperoxide or H2O2 as oxidant. Characterization results showed that dioxomolybdenum(VI) complex was successfully grafted onto the amino-functionalized graphene oxide and the structure of the graphene oxide was well preserved after several stepwise synthesis procedures. Catalytic tests showed that heterogeneous catalyst MoO2-salen-GO was more active than its homogeneous analogue MoO 2-salen in the epoxidation of cyclooctene due to site isolation. In addition, the MoO2-salen-GO catalyst could be reused three times without significant loss of activity.
Synthesis and biological imaging of fluorescent polymeric nanoparticles with AIE feature via the combination of RAFT polymerization and post-polymerization modification
Liu, Yanzhu,Mao, Liucheng,Yang, Saijiao,Liu, Meiying,Huang, Hongye,Wen, Yuanqing,Deng, Fengjie,Li, Yongxiu,Zhang, Xiaoyong,Wei, Yen
, p. 79 - 87 (2018)
In recent years, florescent polymeric nanoparticles (FPNs) containing aggregation-induced emission (AIE) fluorogens have received great intention for their potential applications in biological imaging and theranostic nanomedicine. Herein, we have developed AIE-active FPNs through a combination of reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer (RAFT) polymerization and post-polymerization modification strategies. The salicylaldehyde (SA) containing zwitterionic copolymers are fabricated via RAFT polymerization and further modified by benzophenone hydrazone (BPH) via Schiff base reaction. The obtained AIE-active amphiphilic copolymers BPH-poly(FHMA-co-MPC) can self-assemble in aqueous solution with the hydrophobic fluorogens aggregating together to form the core and the hydrophilic chains to form the protective shell. BPH-poly(FHMA-co-MPC) and the resulting FPNs are characterized by 1H nuclear magnetic resonance spectroscopy, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, transmission electron microscopy and fluorescence spectroscopy. Results demonstrate that BPH-poly(FHMA-co-MPC) are successfully synthesized and as-prepared BPH-poly(FHMA-co-MPC) FPNs exhibit desirable morphology and size, good dispersibility, high brightness, remarkable photostability and large Stokes shifts. More importantly, through cytotoxicity test and cell uptake behavior, these BPH-poly(FHMA-co-MPC) FPNs show low toxicity and excellent cell dyeing behavior. Taken together, we have developed a facile and effective method for the fabrication of AIE-active FPNs, which display great potential for biomedical applications.
Rhodium(III)-Catalyzed C-H/N-H Alkyne Annulation of Nonsymmetric 2-Aryl (Benz)imidazole Derivatives: Photophysical and Mechanistic Insights
Dias, Gleiston G.,Paz, Esther R. S.,Kadooca, Juliana Y.,Sabino, Ad?o A.,Cury, Luiz A.,Torikai, Kohei,De Simone, Carlos A.,Fantuzzi, Felipe,Da Silva Júnior, Eufranio N.
, p. 264 - 278 (2021/01/09)
Rhodium(III) catalysis enabled C-H/N-H alkyne annulation of nonsymmetric imidazole derivatives. This study encompasses the synthesis of imidazoles from a naturally occurring quinoidal compound and their use for the preparation of rigid π-extended imidazole derivatives with outstanding fluorescence. Our study also brings to light the photophysical aspects and the mechanism of the reaction studied via computational calculations. This method provided an efficient and versatile tool for the synthesis of fluorescent compounds with a wide range of chemical and biological applications.
Introduction of a trinuclear manganese(iii) catalyst on the surface of magnetic cellulose as an eco-benign, efficient and reusable novel heterogeneous catalyst for the multi-component synthesis of new derivatives of xanthene
Ghamari Kargar, Pouya,Bagherzade, Ghodsieh,Eshghi, Hossein
, p. 4339 - 4355 (2021/02/03)
In this work, the new trinuclear manganese catalyst defined as Fe3O4@NFC@NNSM-Mn(iii) was successfully manufactured and fully characterized by different techniques, including FT-IR, XRD, TEM, SEM, EDX, VSM, and ICP analysis. There have been reports of the use of magnetic catalysts for the synthesis of xanthine derivatives. The critical potential interest in the present method include short reaction time, high yields, recyclability of the catalyst, easy workup, and the ability to sustain a variety of functional groups, which give economical as well as ecological rewards. Also, the synthesized catalyst was used as a recyclable trinuclear catalyst in alcohol oxidation reactions at 40 °C. The magnetic catalyst activity of Fe3O4@NFC@NNSM-Mn(iii) could be attributed to the synergistic effects of the catalyst Fe3O4@NFC@NNS-Mn(iii) with melamine. Employing a sustainable and safe low temperature, using an eco-friendly solvent, no need to use any additive, and long-term stability and magnetic recyclability of the catalyst for at least six successive runs are the advantages of the current protocol towards green chemistry. This protocol is a benign, environmentally friendly method for heterocycle synthesis. This journal is
The anchoring of a Cu(ii)-salophen complex on magnetic mesoporous cellulose nanofibers: green synthesis and an investigation of its catalytic role in tetrazole reactions through a facile one-pot route
Bagherzade, Ghodsieh,Ghamari kargar, Pouya
, p. 19203 - 19220 (2021/06/03)
Today, most synthetic methods are aimed at carrying out reactions under more efficient conditions and the realization of the twelve principles of green chemistry. Due to the importance and widespread applications of tetrazoles in various industries, especially in the field of pharmaceutical chemistry, and the expansion of the use of nanocatalysts in the preparation of valuable chemical reaction products, we decided to use an (Fe3O4@NFC@NSalophCu)CO2H nanocatalyst in this project. In this study, the synthesis of the nanocatalyst (Fe3O4@NFC@NSalophCu)CO2H was explained in a step-by-step manner. Confirmation of the structure was obtained based on FT-IR, EDX, FE-SEM, TEM, XRD, VSM, DLS, TGA, H-NMR, and CHNO analyses. The catalyst was applied to the synthesis of 5-substituted-1H-tetrazole and 1-substituted-1H-tetrazole derivatives through multi-component reactions (MCRs), and the performance was assessed. With advances in science and technology and increasing environmental pollution, the use of reagents and methods that are less dangerous for the environment has received much attention. Therefore, following green chemistry principles, with the help of the (Fe3O4@NFC@NSalophCu)CO2H salen complex as a nanocatalyst that is recyclable, cheap, safe, and available, the use of water as a green solvent, and reduced reaction times, the synthesis of tetrazoles can be achieved.