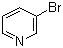
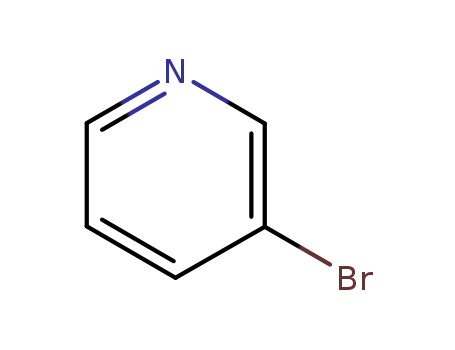
3-Pyridyl bromide literature
Photorelease of Pyridines Using a Metal-Free Photoremovable Protecting Group
Dong, Zaizai,Fang, Xiaohong,Kou, Xiaolong,Tan, Weihong,Tang, Xiao-Jun,Wu, Yayun,Zhang, Zhen,Zhao, Rong,Zhou, Wei
supporting information, p. 18386 - 18389 (2020/08/24)
The photorelease of bioactive molecules has emerged as a valuable tool in biochemistry. Nevertheless, many important bioactive molecules, such as pyridine derivatives, cannot benefit from currently available organic photoremovable protecting groups (PPGs). We found that the inefficient photorelease of pyridines is attributed to intramolecular photoinduced electron transfer (PET) from PPGs to pyridinium ions. To alleviate PET, we rationally designed a strategy to drive the excited state of PPG from S1 to T1 with a heavy atom, and synthesized a new PPG by substitution of the H atom at the 3-position of 7-dietheylamino-coumarin-4-methyl (DEACM) with Br or I. This resulted in an improved photolytic efficiency of the pyridinium ion by hundreds-fold in aqueous solution. The PPG can be applied to various pyridine derivatives. The successful photorelease of a microtubule inhibitor, indibulin, in living cells was demonstrated for the potential application of this strategy in biochemical research.
Catalyst-Free N-Deoxygenation by Photoexcitation of Hantzsch Ester
Cardinale, Luana,Jacobi Von Wangelin, Axel,Konev, Mikhail O.
supporting information, (2020/02/15)
A mild and operationally simple protocol for the deoxygenation of a variety of heteroaryl N-oxides and nitroarenes has been developed. A mixture of substrate and Hantzsch ester is proposed to result in an electron donor-acceptor complex, which upon blue-light irradiation undergoes photoinduced electron transfer between the two reactants to afford the products. N-oxide deoxygenation is demonstrated with 22 examples of functionally diverse substrates, and the chemoselective reduction of nitroarenes to the corresponding hydroxylamines is also shown.
Base-catalyzed aryl halide isomerization enables the 4-selective substitution of 3-bromopyridines
Bandar, Jeffrey S.,Puleo, Thomas R.
, p. 10517 - 10522 (2020/10/18)
The base-catalyzed isomerization of simple aryl halides is presented and utilized to achieve the 4-selective etherification, hydroxylation and amination of 3-bromopyridines. Mechanistic studies support isomerization of 3-bromopyridines to 4-bromopyridines proceedsviapyridyne intermediates and that 4-substitution selectivity is driven by a facile aromatic substitution reaction. Useful features of a tandem aryl halide isomerization/selective interception approach to aromatic functionalization are demonstrated. Example benefits include the use of readily available and stable 3-bromopyridines in place of less available and stable 4-halogenated congeners and the ability to converge mixtures of 3- and 5-bromopyridines to a single 4-substituted product.
Synthesis method of 3-bromopyridine
-
Paragraph 0017-0024, (2020/05/05)
The invention belongs to the field of organic synthesis, and particularly relates to a synthesis method of 3-bromopyridine. The synthesis method comprises the following steps: (1) dropwise adding bromine into pyridine and 80-95% sulfuric acid at 0 DEG C, and reacting at 130-140 DEG C for 7-8 hours; (2) after the reaction is finished, cooling, pouring into ice water, and regulating the pH value to8 by using 6N sodium hydroxide; and (3) extracting with an organic solvent, layering, drying, filtering, concentrating and distilling. The method has the beneficial effects of high yield, mild reaction conditions, simple reaction steps and simple and easily available raw materials, and is suitable for industrial production.