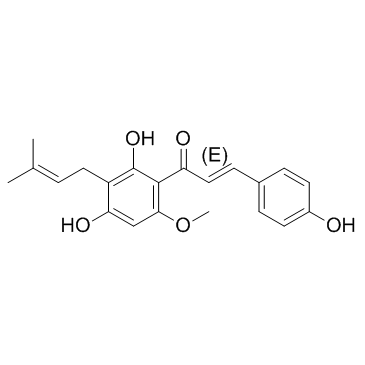
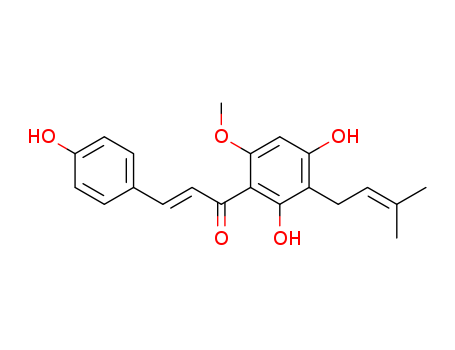
Xanthohumol literature
Synthesis of xanthohumol and xanthohumol-d3from naringenin
?cianowski, Jacek,Andrusiak, Joanna,Budny, Marcin,Mylkie, Kinga,Wolan, Andrzej,Wysocka, Ma?gorzata
, p. 28934 - 28939 (2021/09/22)
A six-step synthesis of xanthohumol (1a) and its d3-derivative (1b) from easily accessible naringenin is reported. The prenyl side chain was introduced by Mitsunobu reaction followed by the europium-catalyzed Claisen rearrangement and base-mediated opening of chromanone gave access to an α,β-conjugated ketone system. Compound1bwas used as an internal standard in stable isotope dilution assays of1ain two Polish beers.
Microbial conjugation studies of licochalcones and xanthohumol
Han, Fubo,Xiao, Yina,Lee, Ik-Soo
, (2021/06/30)
Microbial conjugation studies of licochalcones (1–4) and xanthohumol (5) were performed by using the fungi Mucor hiemalis and Absidia coerulea. As a result, one new glucosylated metabolite was produced by M. hiemalis whereas four new and three known sulfated metabolites were obtained by transformation with A. coerulea. Chemical structures of all the metabolites were elucidated on the basis of 1D-, 2D-NMR and mass spectroscopic data analyses. These results could contribute to a better understanding of the metabolic fates of licochalcones and xanthohumol in mammalian systems. Although licochalcone A 4′-sulfate (7) showed less cytotoxic activity against human cancer cell lines compared to its substrate licochalcone A, its activity was fairly retained with the IC50 values in the range of 27.35–43.07 μM.
Synthesis and Antiproliferative Activity of Prenylated Chalcone Mannich Base Derivatives
Han, Pei-Pei,Liu, Ke-Xiong,Su, Liang,Wang, Qiu-An
, p. 425 - 431 (2021/05/29)
Prenylated chalcones xanthohumol (1) and 2′-hydroxy-3,4,4′-trimethoxy-6′-O-prenyl chalcone (2) were synthesized through the Claisen–Schmidt condensation, O-prenylation, and Claisen rearrangement and deprotection respectively, using phloroglucinol and appropriate benzaldehydes as starting materials. Based on the Mannich reaction of prenylated chalcone 1 or 2 with various secondary amines and formaldehyde in acid alcohol solvent, 10 novel prenylated chalcone Mannich base derivatives 3a–3e and 4a–4e were synthesized. Furthermore, all synthetic compounds were evaluated for antiproliferative activities in vitro against four human cancer cell lines (Aspc-1, SUN-5, HepG-2, and HCT-116) by MTT assay. The results showed that most of them exhibit moderate to good antiproliferative activities against the four human cancer cells with IC50 values of 2.52 to 47.67 μM.
Synthesis of xanthohumol analogues and discovery of potent thioredoxin reductase inhibitor as potential anticancer agent
Zhang, Baoxin,Duan, Dongzhu,Ge, Chunpo,Yao, Juan,Liu, Yaping,Li, Xinming,Fang, Jianguo
supporting information, p. 1795 - 1805 (2015/04/27)
The selenoprotein thioredoxin reductases (TrxRs) are attractive targets for anticancer drugs development. Xanthohumol (Xn), a naturally occurring polyphenol chalcone from hops, has received increasing attention because of its multiple pharmacological activities. We synthesized Xn and its 43 analogues and discovered that compound 13n displayed the highest cytotoxicity toward HeLa cells (IC50 = 1.4 μM). Structure-activity relationship study indicates that the prenyl group is not necessary for cytotoxicity, and introducing electron-withdrawing group, especially on the meta-position, is favored. In addition, methylation of the phenoxyl groups generally improves the potency. Mechanistic study revealed that 13n selectively inhibits TrxR and induces reactive oxygen species and apoptosis in HeLa cells. Cells overexpressing TrxR are resistant to 13n insult, while knockdown of TrxR sensitizes cells to 13n treatment, highlighting the physiological significance of targeting TrxR by 13n. The clarification of the structural determinants for the potency would guide the design of novel potent molecules for future development.