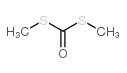
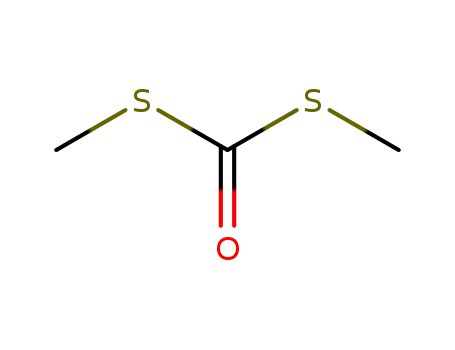
S,S'-Dimethyl dithiocarbonate literature
Trifluoroacetic Acid Catalysed Rearrangement of Dialkyl Xanthates to Dithiocarbonates with Inversion of Configuration
Fichtner, Michael W.,Haley, Neil F.
, p. 3141 - 3143 (1981)
-
Trithioorthoester Exchange and Metathesis: New Tools for Dynamic Covalent Chemistry
Bothe, Michael,Furlan, Ricardo L. E.,Orrillo, A. Gastón,Von Delius, Max
supporting information, p. 1988 - 1994 (2019/10/22)
To expand the toolbox of dynamic covalent and systems chemistry, we investigated the acid-catalyzed exchange reaction of trithioorthoesters with thiols. We found that trithioorthoester exchange occurs readily in various solvents in the presence of stoichiometric amounts of strong Bronsted acids or catalytic amounts of certain Lewis acids. The scope of the exchange reaction was explored with various substrates, and conditions were identified that permit clean metathesis reactions between two different trithioorthoesters. One distinct advantage of S, S, S-orthoester exchange over O, O, O-orthoester exchange is that the exchange reaction can kinetically outcompete hydrolysis, thereby making the process less sensitive to residual moisture. We expect that the relatively high stability of the products might be beneficial in future supramolecular receptors or porous materials.
Identification and biosynthesis of tropone derivatives and sulfur volatiles produced by bacteria of the marine Roseobacter clade
Thiel, Verena,Brinkhoff, Thorsten,Dickschat, Jeroen S.,Wickel, Susanne,Grunenberg, Joerg,Wagner-Doebler, Irene,Simon, Meinhard,Schulz, Stefan
experimental part, p. 234 - 246 (2010/04/29)
Bacteria of the Roseobacter clade are abundant marine bacteria and are important contributors to the global sulfur cycle. The volatiles produced by two of its members, Phaeobacter gallaeciensis and Oceanibulbus indolifex, were analyzed to investigate whether the released compounds are derived from sulfur metabolism, and which biosynthetic pathways are involved in their formation. Both bacteria emitted different sulfides and thioesters, including new natural compounds such as 5-methyl phenylethanethioate (16) and butyl methanesulfonate (21). The S-methyl alkanoates were identified by comparison with standards that were synthesized from the respective methyl alkanoates by a new method using an easily prepared aluminium/sulfur reagent. Phaeobacter gallaeciensis is also able to produce tropone (37) in large amounts. Its biosynthesis was investigated by various feeding experiments, showing that 37 is formed via a deviation of the phenylacetate catabolism. The unstable tropone hydrate 42 was identified as an intermediate of the tropone biosynthesis that was also released together with tropolone (38). The Royal Society of Chemistry 2010.
A facile, safe and inexpensive preparation of S -methyl arylcarbamothioates by methylthiocarbonylation of primary arylamines with O, S -dimethyl carbonodithioate
Degani, Iacopo,Fochi, Rita,Magistris, Claudio
experimental part, p. 1113 - 1122 (2010/05/19)
O,S-Dimethyl carbonodithioate is proposed as a suitable and safely handled reagent that can be used in the methylthiocarbonylation of primary arylamines to give S-methyl arylcarbamothioates. Optimal conditions involved a one-step procedure that was carried out at 45C in a solvent-free system, in the presence of triethyl(methyl)ammonium S-methyl carbonodithioate as a reaction promoter. The title products were obtained pure in yields that, with one exception, varied between 72 and 91% (average yield of the 12 considered examples was 83%). The by-product S,S-dimethyl carbonodithioate is also a valuable reagent. Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart · New York.
O,S-Dimethyl carbonodithioate as a phosgene substitute for the preparation of S-methyl alkylcarbamothioates and dialkylcarbamothioates
Degani, Iacopo,Fochi, Rita,Magistris, Claudio
experimental part, p. 3807 - 3818 (2010/03/30)
O,S-Dimethyl carbonodithioate is proposed as a suitable and safely handled reagent that can be used as a replacement for phosgene in the synthesis of S-methyl alkyl- and dialkylcarbamothioates. The former were obtained by a two-step procedure, which can also be carried out in a one-pot fashion without isolating the intermediates O-methyl alkylcarbamothioates; the overall yields of the pure S-methyl alkylcarbamothioates were 94-98%. Optimal conditions for the synthesis of S-methyl dialkylcarbamothioates involved a one-step procedure in a solvent-free system in the presence of triethyl(methyl)ammonium methyl carbonate as a catalyst; yields of the pure products were 85-98%. A mechanism is proposed for the carbamothioate-formation reaction. Georg Thieme Verlag Stuttgart.