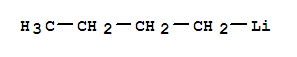n-Butyllithium literature
-
Tomboulian,Stehower
, p. 1509 (1968)
-
Relative Reactivities and Mechanistic Aspects of the Reactions of Organic Halides with Alkali Metals in Alcohol Environments
Reynolds, J. L.,Doshi, D.,Shechter, H.
, p. 8032 - 8041 (1987)
The relative reactivities of organic halides over wide concentration ranges have been determined with limited amounts of lithium, sodium, and potassium in 2-ethoxyethanol (1) at 0 deg C.Under these conditions the organometallics formed protonate to their hydrocarbons rather than undergo exchange, elimination, and simple or crossed coupling.In dilute solution in 1 the relative reactivities (r1/r2) of varied halides with lithium are essentially structure independent.However, as the concentrations of the halides increase, their relative reactivities become significantly different and depend on the total concentrations T (M) = 1X> + 2X>> of the organic halides.With lithium at increased halide concentrations (1) the reactivities are iodides > bromides > chlorides, (2) halides of lower molecular weight react more rapidly than their higher homologues, and (3) the reactivity orders of chlorides are (a) allyl > primary > secondary > tertiary > neopentyl, (b) 2-buten-1-yl > 1-buten-3-yl, (c) benzyl > phenyl, and (d) p-chlorotolyl > o-chlorotolyl > m-chlorotolyl.As examples, the relative reactivities of 1-chlorobutane/2-chloro-2-methylpropane (CT = 5.83 M), 3-chloropropene/1-bromobutane (CT = 4.60 M), bromobenzene/p-chlorotoluene (CT = 4.37 M), and benzyl chloride/chlorobenzene (CT = 4.02 M) are 6.71, 5.43, 24.1, and 22.1, respectively.Additions of aprotic solvents to 1-chlorobutane and 2-chloro-2-methylpropane in 1 decrease the relative reactivities of the halides.The effectiveness of cosolvents in lowering the relative reactivities of lithium with 1-chlorobutane and 2-chloro-2-methylbutane is tetrahydrofuran > dioxane ca. 2-ethoxyethanol (1) > cyclohexene ca. benzene.The relative reactivities of halides with sodium and with potassium in 1 at 0 deg C are also total halide concentration (CT) dependent.Under comparable concentrations the relative reactivity differences of halides are greater with lithium than sodium than potassium.The reactivities of halides under conditions of chemical control can be correlated with the ionization potentials of the alkali metals, and the kinetically controlling features of these systems are different from those with magnesium.The behavior of the alkali metals, the effects of concentration, and the roles of solvents on the reactivities of halides are discussed on the basis of (1) the active sites on the metal surfaces as modified by induction and (2) steric and electronic factors in the organic substrates.The kinetically controlled reactions of lithium with sp3 halides may be interpreted to invole formation of lithio organohalide radical anions (R.-X(1-), Li(1+)), electron transfer to the lithio radical anions on the metal surface, or unsymmetrical four-center carbanionic processes on the metal.In addition to incorporating an electron into the lowest unoccupied ? level of its C-X bond, an sp2 halide offers the possibility for kinetically controlling electron transfer into the ? system of its carbon-carbon double bond(s).
-
Gilman,Zoellner,Selby
, (1933)
-
Ultrasounds in Organic Syntheses. 1. Effect on the Formation of Lithium Organometallic Reagents
Luche, Jean-Louis,Damiano, Jean-Claude
, p. 7926 - 7927 (1980)
-
Inhibitors of viral replication, their process of preparation and their therapeutical uses
-
Page/Page column, (2014/05/06)
The present invention relates to compounds, their use in the treatment or the prevention of viral disorders, including HIV.
Fine-tuning the oxidative ability of persistent radicals: Electrochemical and computational studies of substituted 2-pyridylhydroxylamines
Bogart, Justin A.,Lee, Heui Beom,Boreen, Michael A.,Jun, Minsik,Schelter, Eric J.
supporting information, p. 6344 - 6349 (2013/07/26)
N-tert-Butyl-N-2-pyridylhydroxylamines were synthesized from 2-halopyridines and 2-methyl-2-nitrosopropane using magnesium-halogen exchange. The use of Turbo Grignard generated the metallo-2-pyridyl intermediate more reliably than alkyllithium reagents. The hydroxylamines were characterized using NMR, electrochemistry, and density functional theory. Substitution of the pyridyl ring in the 3-, 4-, and 5-positions was used to vary the potential of the nitroxyl/oxoammonium redox couple by 0.95 V. DFT computations of the electrochemical properties agree with experiment and provide a toolset for the predictive design of pyridyl nitroxides.
Catalyst component, catalyst for olefin polymerization, and process for producing olefin polymer using catalyst
-
, (2012/08/29)
A polymer having high catalyst activity, excellent hydrogen response, high stereoregularity and high yield can be obtained by polymerizing olefins in the presence of a catalyst for olefin polymerization comprising (A) a solid catalyst component containing magnesium, titanium, a halogen, and an electron donor compound, (B) an organoaluminum compound shown by the formula R6pAlQ3-p(R1R2N)m, and (C) an aminosilane compound shown by the formula (R3HN)nR4pSi(OR5)q.
MATERIAL FOR ORGANIC ELECTRO-OPTICAL DEVICE HAVING FLUORENE DERIVATIVE COMPOUND AND ORGANIC ELECTRO-OPTICAL DEVICE INCLUDING THE SAME
-
, (2010/08/07)
The present invention relates to a material for an organic electro-optical device and an organic electro-optical device including the same. More particularly, the present invention relates to a material having thermal stability of a glass transition temperature of 120° C. or more and a thermal decomposition temperature of 450° C. or more, and being capable of providing an organic electro-optical device having high efficiency and a long life-span due to less crystallization and improved amorphous properties in a material for an organic electro-optical device. The material for an organic electro-optical device can be used singularly or as a host material in combination with a dopant, and includes an asymmetric fluorene derivative compound. An organic electro-optical device including the material for an organic electro-optical device is also provided.