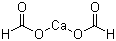Calcium formate literature
Hydrogenation of aqueous mixtures of calcium carbonate and carbon dioxide using a water-soluble rhodium(I)-tertiary phosphine complex catalyst
Jószai, István,Joó, Ferenc
, p. 87 - 91 (2004)
Aqueous suspensions of calcium carbonate were hydrogenated to yield calcium formate under a gas phase containing both H2 and CO2. A rhodium(I)-complex of monosulfonated triphenylphosphine (mtppms), [RhCl(mtppms)3] was used as catalyst. Reaction temperatures were in the range of 20-70°C, total pressure 10-100 bar with an optimum p(CO 2):p(H2) ratio of 1:4. Due to the mobile bicarbonate-formate equilibrium, the highest available formate concentration is decreased with increasing temperature but increased with increasing pressure. Interestingly, at 50°C and 100 bar total pressure the yield of formate was 143% (based on CaCO3) which implies the formation of free formic acid in the reaction of CO2 from the gas phase. The dependence of the hydrogenation rate on the catalyst and ligand concentrations, as well as that of the decomposition of formate as a function of temperature were also studied. A mild method has been developed for the hydrogenation of calcium carbonate to calcium formate in aqueous suspensions under CO2 + H2 pressure catalyzed by [RhCl(mtppms)3] (mtppms = monosulfonated triphenylphosphine) at 20-70°C and 10-100 bar total pressure. In certain cases the yield of formate exceeded 100% (based on CaCO3) which implies the concomitant hydrogenation of carbon dioxide, too.
-
Balcerowiak, W.,Terelak, K.,Trybula, S.
, p. 1231 - 1238 (1995)
-
Eco-friendly upconversion of limestone into value-added calcium formate
Gunasekar, Gunniya Hariyanandam,Padmanaban, Sudakar,Park, Hongjin,Yoon, Sungho
, p. 4995 - 5001 (2020)
Although CaCO3 is a naturally available, inexpensive, abundant and extensively used chemical in various industries, to date, most of its conversions liberate CO2 into the atmosphere, which accounts for about 5-6% of global anthropogenic CO2 emission. Herein, the first synthesis of calcium formate (CF) by hydrogenation of an aqueous mixture of CaCO3 and CO2 using a heterogeneous catalyst in an unconventional CO2 reducing manner is reported. The phosphine-based heterogenized Ru catalyst efficiently converts CaCO3 into CF with good selectivity (>99%) and is readily separated from the reaction product, resulting in promising recycling ability. Thus, this work provides a promising strategy for the design of green and sustainable conversion of carbonate minerals in industry.
Eco-friendly and techno-economic conversion of CO2 into calcium formate, a valuable resource
Lee, Chul-Jin,Yoon, Ha-Jun,Yoon, Hayoung,Yoon, Sungho,Yoon, Taeksang
, p. 1738 - 1745 (2022/03/08)
The suppression of greenhouse gas emissions is being considered more important than ever, and consequently, the development of methods to produce useful CO2 conversion products with excellent techno-economic feasibility and high CO2 reduction capability is of interest. A continuous CO2 conversion system and a heterogenized hydrogenation catalyst can be used to develop a process for the efficient and selective production of Ca(HCO2)2, which has not been considered as a CO2 conversion product so far, from waste resources, including CaO. Techno-economic analysis of the entire process showed that the production cost of Ca(HCO2)2 was reduced by around 16% compared with the conventional process, indicating a high possibility of market penetration. Furthermore, the estimation of the global warming index of the process through a life-cycle assessment showed that the global warming index could be reduced by about 20% compared with that of existing Ca(HCO2)2 production processes.
A a method of preparing calcium
-
Paragraph 0022-0023, (2017/07/07)
The invention discloses a preparation method of calcium formate and belongs to the technical field of chemical synthesis. The preparation method of the calcium formate comprises the following steps: carrying out dust removal on semi-water gas, desulphurizing, compressing, carbonizing and recompressing to 3-5MPa to obtain feed gas, reacting with a calcium hydroxide turbid liquid in the presence of ammonia or amine to generate a calcium formate aqueous solution containing ammonium formate or amine formate, adding right amount of lime milk and carrying out a replacement reaction in a calcium formate aqueous solution concentrating process, so that calcium formate precipitate is obtained. The preparation method of the calcium formate has the advantages that a reaction accelerator volatile alkali is used in a process that the feed gas reacts with the calcium hydroxide turbid liquid, generation of formate ions in reaction between carbon monoxide and hydroxyl ions is sped up, and concentration of a formate solution generated by the reaction between the carbon monoxide and hydroxyl ions is greatly increased, so that energy consumption in a concentration process is reduced, and coproduction of calcium formate and sodium formate can be realized on the basis of the original synthetic ammonia production system.
CO2-"Neutral" hydrogen storage based on bicarbonates and formates
Boddien, Albert,Gaertner, Felix,Federsel, Christopher,Sponholz, Peter,Mellmann, Doerthe,Jackstell, Ralf,Junge, Henrik,Beller, Matthias
, p. 6411 - 6414 (2011/08/05)
Let the circle be unbroken! One ruthenium catalyst generated in situ facilitates the selective hydrogenation of bicarbonates and carbonates, as well as CO2 and base, to give formates and also the selective dehydrogenation of formates back to bicarbonates. The two reactions can be coupled, leading to a reversible hydrogen-storage system. dppm=1,2- bis(diphenylphosphino)methane. Copyright