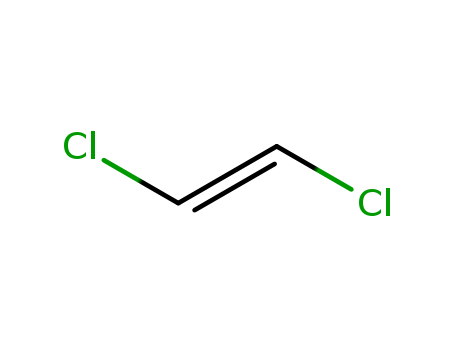
trans-1,2-Dichloroethylene literature
ArF laser photolytic deposition and thermal modification of an ultrafine chlorohydrocarbon
Pola, Josef,Galikova, Anna,Subrt, Jan,Ouchi, Akihiko
, p. 625 - 629 (2010)
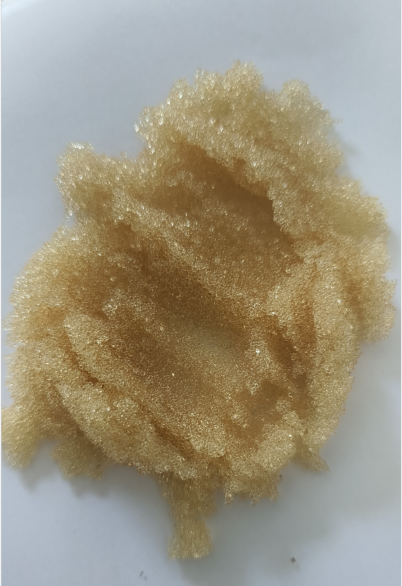
MW ArF laser irradiation of gaseous cis-dichloroethene results in fast decomposition of this compound and in deposition of solid ultrafine Cl- and H-containing carbonaceous powder which is of interest due to its sub-microscopic structure and possible reactive modification of the C-Cl bonds. The product was characterized by electron microscopy, and FTIR and Raman spectra and it was revealed that HCl, H2, and C/H fragments are lost and graphitic features are adopted upon heating to 700°C.
Reductive capacity of natural reductants
Lee, Woojin,Batchelor, Bill
, p. 535 - 541 (2003)
The reductive capacities of soil minerals and Silawa soil for Cr(VI) and chlorinated ethylenes were determined and characterized to understand in situ treatment using these natural reductions. The reductive capacity of soil minerals for Cr(VI) was 3-16 times greater than that for tetrachloroethylene (PCE), indicating that Cr(VI) is more susceptible to the reduction by soil minerals than PCE. Green rust (GRSO4) showed the greatest reductive capacity for Cr(VI) and PCE followed by magnetite, pyrite, biotite, montmorillonite, and vermiculite. The major transformation product in pyrite and GRSO4 suspensions was acetylene rather than dichloroethylene (DCE) and vinyl chloride (VC). For VC degradation, ethylene was the main transformation product with a low concentration of ethane observed. Fe(II) content in soil minerals was directly proportional to the reductive capacity of soil minerals for Cr(VI) and PCE, suggesting that Fe(II) content is an important factor that significantly affects reductive transformations of target contaminants in natural systems.
Mercury-photosensitized reactions of cis-2-butene-ethanol and cis-2-butene-propylamine mixtures
Yamamoto,Kasamatsu,Sueishi
, p. 3934 - 3938 (2001)
The Hg(3P1)-photosensitized luminescence of propylamine (PA) and ethanol (ET) and the Hg(3P1)-photosensitized isomerization of cis-2-butene (cis-2B) were studied in ET-cis-2B and PA-cis-2B mixtures under steady illumination at room temperature. The decreases in intensities of the luminescence from the HgPA* and HgET* complexes by adding cis-2B were much steeper than those anticipated by the competitive quenching of Hg(3P1) by PA (ET) and cis-2B. However, the decreases of the isomerization rate of cis-2B by additions of ET and PA were smaller than those expected by the competitive quenching by PA (ET) and cis-2B. The findings for PA-cis-2B mixtures could be explained by considering the addition reaction Hg(3P0) + cis-2B → Hg(1S0) + B* (B* = triplet state of 2-butene). Although HgCl formation was predominant and no cis-trans isomerization was observed in the Hg(3P1)-photosensitized reaction of cis- and trans-1,2-dichloroethylene (DCE) the isomerization of DCE in the photosensitized reaction of DCE-ET [DCE]0:[ET]0 = 1:100) mixture could be followed. These results could also be explained by the reaction HgET* + DCE → Hg(1S0) + ET + DCE*. This kind of reaction was proposed for the first time.
-
Rabinovich,Hulatt
, p. 592 (1957)
-
Preparation and reactivity of vitaminB12-TiO2 hybrid catalyst immobilized on a glass plate
Shimakoshi, Hisashi,Abiru, Makoto,Kuroiwa, Keita,Kimizuka, Nobuo,Watanabe, Midori,Hisaeda, Yoshio
experimental part, p. 170 - 172 (2010/05/15)
The vitaminB12-TiO2 hybrid catalyst was effectively immobilized on a glass plate, and the immobilized catalyst shows an efficient reactivity for various molecular transformations, such as the 1,2-migration of a phenyl group and dechlorination of perchloroethylene during irradiation by UV light.
Composition For the Vapor Phase Dehydrohalogenation of 1,1,2-Trihaloethane To 1,1-Dihaloethylene and Methods For Preparing and Using Such Composition
-
Page/Page column 7, (2008/12/07)
Described are compositions adapted to catalyze the vapor phase dehydrohalogenation of 1,1,2-trihaloethane to 1,1-dihaloethylene, e.g., 1,1,2-trichloroethane to vinylidene chloride. These materials include activated carbon and at least one benzimidazole-containing material defined herein as including benzimidazole, a derivative thereof, a salt thereof or mixtures thereof. Also described are methods for producing and using these catalytic compositions.
COMPOSITION FOR THE VAPOR PHASE DEHYDROHALOGENATION OF 1,1,2-TRIHALOETHANE TO 1,1-DIHALOETHYLENE AND METHODS FOR PREPARING AND USING SUCH COMPOSITIONS
-
Page/Page column 16-27; 31-32, (2010/11/25)
Described are compositions adapted to catalyze the vapor phase dehydrohalogenation of 1,1,2-trihaloethane to 1,1-dihaloethylene, e.g., 1,1,2-trichloroethane to vinylidene chloride. These materials include activated carbon and at least one benzimidazole-containing material defined herein as including benzimidazole, a derivative thereof, a salt thereof or mixtures thereof. Also described are methods for producing and using these catalytic compositions.